Odločanje je najpomembnejši vidik skoraj vseh programskih jezikov. Kot pove že ime, nam odločanje omogoča izvajanje določenega bloka kode za določeno odločitev. Tu se odloča o veljavnosti posameznih pogojev. Preverjanje stanja je hrbtenica odločanja.
zeenat aman igralec
V pythonu sprejemanje odločitev poteka z naslednjimi stavki.
| Izjava | Opis |
|---|---|
| Izjava Če | Stavek if se uporablja za testiranje določenega pogoja. Če je pogoj resničen, se izvede blok kode (if-block). |
| Izjava if – else | Stavek if-else je podoben stavku if, razen dejstva, da zagotavlja tudi blok kode za napačen primer pogoja, ki ga je treba preveriti. Če je pogoj v stavku if napačen, se izvede stavek else. |
| Ugnezdeni stavek if | Ugnezdeni stavki if nam omogočajo uporabo if? stavek else znotraj zunanjega stavka if. |
Zamik v Pythonu
Zaradi lažjega programiranja in doseganja preprostosti python ne dovoljuje uporabe oklepajev za kodo na ravni bloka. V Pythonu se za deklaracijo bloka uporablja zamik. Če sta dva stavka na isti ravni zamika, potem sta del istega bloka.
Na splošno so štirje presledki podani za zamik stavkov, kar je tipična količina zamika v pythonu.
Zamik je najpogosteje uporabljen del jezika python, saj deklarira blok kode. Vsi stavki enega bloka so predvideni na isti ravni zamika. Videli bomo, kako poteka dejanski zamik pri odločanju in drugih stvareh v pythonu.
Stavek if
Stavek if se uporablja za testiranje določenega pogoja in če je pogoj resničen, izvede blok kode, znan kot if-block. Pogoj stavka if je lahko kateri koli veljaven logični izraz, ki ga je mogoče ovrednotiti kot resničnega ali napačnega.
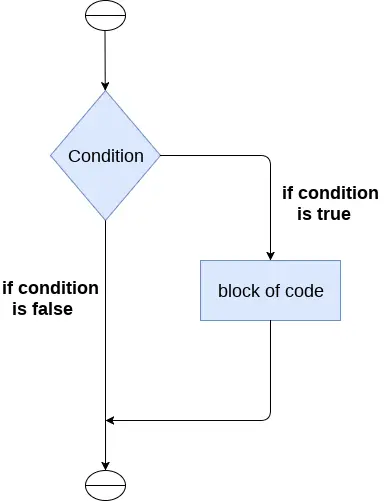
Sintaksa if-stavka je podana spodaj.
vse velike črke ukaz excel
if expression: statement
Primer 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
Izhod:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
Primer 2 : Program za tiskanje največjega od treh števil.
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
Izhod:
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
Stavek if-else
Stavek if-else zagotavlja blok else v kombinaciji s stavkom if, ki se izvede v napačnem primeru pogoja.
Če je pogoj resničen, se izvede blok if. V nasprotnem primeru se izvede blok else-block.

Sintaksa stavka if-else je podana spodaj.
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
Primer 1 : Program za preverjanje, ali je oseba upravičena do glasovanja ali ne.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
Izhod:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Primer 2: Program za preverjanje, ali je število sodo ali ne.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
Izhod:
10 od 1 milijona
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
Izjava elif
Stavek elif nam omogoča, da preverimo več pogojev in izvedemo določen blok stavkov glede na pravi pogoj med njimi. V našem programu imamo lahko poljubno število stavkov elif, odvisno od naših potreb. Vendar uporaba elif ni obvezna.
Stavek elif deluje kot lestvični stavek if-else-if v C. Naslediti ga mora stavek if.
Sintaksa stavka elif je podana spodaj.
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

Primer 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
Izhod:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Primer 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 