Glede na samsko povezan seznam je naloga izbrisati srednje vozlišče seznama.
- Če seznam vsebuje enakomerno število vozlišč, bosta dve srednji vozlišči. V tem primeru izbrišite drugo srednje vozlišče.
- Če je povezan seznam sestavljen iz samo enega vozlišča, se vrne NULL.
Primer:
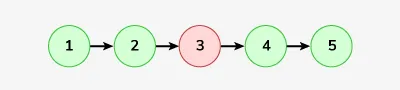
Vnos: LinkedList: 1-> 2-> 3-> 4-> 5
Izhod: 1-> 2-> 4-> 5
Pojasnilo:
Vnos: LinkedList: 2-> 4-> 6-> 7-> 5-> 1
Izhod: 2-> 4-> 6-> 5-> 1
Pojasnilo: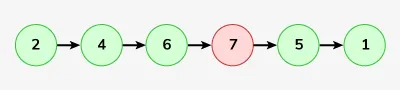
Vnos: LinkedList: 7
Izhod:
Tabela vsebine
- [Naivni pristop] Uporaba dvoprepustnega prehoda - o (n) časa in o (1) prostora
- [Pričakovani pristop] Enopresodočja prehod s počasnimi in hitrimi kazalci - o (n) časom in o (1) prostorom
[Naivni pristop] Uporaba dvoprepustnega prehoda - o (n) časa in o (1) prostora
Osnovna ideja tega pristopa je, da najprej prečkate celoten povezan seznam, da se šteje skupno število vozlišč. Ko poznamo skupno število vozlišč, lahko izračunamo položaj srednjega vozlišča, ki je na indeksu n/2 (kjer je n skupno število vozlišč). Nato spet pojdite na povezan seznam, vendar se tokrat ustavimo tik pred srednjim vozliščem. Ko smo tam spremenili naslednji kazalec vozlišča pred srednjim vozliščem
Spodaj je izvedba zgornjega pristopa:
C++// C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// C program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// Java program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } public class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. public static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next == null) return null; int count = 0; Node p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 != null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward predecessor // of the middle node. for (int i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } public static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println('null'); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.print('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); System.out.print ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
# Python3 program to delete middle of a linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list. def deleteMid(head): # Edge case: return None if there is only # one node. if head.next is None: return None count = 0 p1 = head p2 = head # First pass count the number of nodes # in the linked list using 'p1'. while p1 is not None: count += 1 p1 = p1.next # Get the index of the node to be deleted. middleIndex = count // 2 # Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor # of the middle node. for i in range(middleIndex - 1): p2 = p2.next # Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next return head def printList(head): temp = head while temp is not None: print(temp.data end=' -> ') temp = temp.next print('None') if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print('Original Linked List:' end=' ') printList(head) # Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head) print('Linked List after deleting the middle node:' end=' ') printList(head)
// C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list. static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next == null) return null; int count = 0; Node p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 != null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. int middleIndex = count / 2; // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for (int i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine('null'); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); Console.Write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); Console.Write ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Function to delete middle node from linked list. function deleteMid(head) { // Edge case: return null if there is only // one node. if (head.next === null) return null; let count = 0; let p1 = head p2 = head; // First pass count the number of nodes // in the linked list using 'p1'. while (p1 !== null) { count++; p1 = p1.next; } // Get the index of the node to be deleted. let middleIndex = Math.floor(count / 2); // Second pass let 'p2' move toward the predecessor // of the middle node. for (let i = 0; i < middleIndex - 1; ++i) p2 = p2.next; // Delete the middle node and return 'head'. p2.next = p2.next.next; return head; } function printList(head) { let temp = head; while (temp !== null) { console.log(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } console.log('null'); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5. let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); console.log('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node. head = deleteMid(head); console.log('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head);
Izhod
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> nullptr
Časovna kompleksnost: O (n). Potrebna sta dva prehoda povezanega seznama
Pomožni prostor: O (1). Dodatni prostor ni potreben.
[Pričakovani pristop] En -pasovna prehod s počasnimi in hitrimi kazalci - o (n) časom in o (1) prostorom
Zgornja rešitev zahtevata dva prehoda povezanega seznama. Srednje vozlišče je mogoče izbrisati z enim prehodom. Ideja je uporaba dveh kazalcev Slow_ptr in fast_ptr . Hiter kazalec premika dve vozlišči naenkrat, medtem ko počasni kazalec premakne eno vozlišče naenkrat. Ko hitri kazalec doseže konec seznama, bo počasen kazalec nameščen na srednjem vozlišču. Nato morate priključiti vozlišče, ki prihaja pred srednjim vozliščem ( Predod ) do vozlišča, ki prihaja po srednjem vozlišču. To učinkovito preskoči nad srednjim vozliščem in ga odstrani s seznama.
Spodaj je izvedba zgornjega pristopa
C++// C++ program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// C program to delete middle of a linked list #include
// Java program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head == null) return null; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if (head.next == null) { return null; } Node prev = null; Node slow_ptr = head; Node fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of list while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this pointslow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println('NULL'); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); System.out.print('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); System.out.print ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
# Python program to delete the middle of a linked list class Node: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to delete middle node from linked list def deleteMid(head): # If the list is empty return None if head is None: return None # If the list has only one node # delete it and return None if head.next is None: return None prev = None slow_ptr = head fast_ptr = head # Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead # and the slow pointer 1 node ahead # until fast pointer reaches end of the list while fast_ptr is not None and fast_ptr.next is not None: fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next # Update prev to hold the previous # slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next # At this point slow_ptr points to middle node # Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next # Return the head of the modified list return head def printList(head): temp = head while temp: print(temp.data end=' -> ') temp = temp.next print('NULL') if __name__ == '__main__': # Create a static hardcoded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) print('Original Linked List: ' end='') printList(head) # Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head) print('Linked List after deleting the middle node: ' end='') printList(head)
// C# program to delete middle of a linked list using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to delete middle node from linked list public static Node deleteMid(Node head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head == null) return null; // If the list has only one node // delete it and return null if (head.next == null) { return null; } Node prev = null; Node slow_ptr = head; Node fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until fast pointer reaches end of the list while (fast_ptr != null && fast_ptr.next != null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous // slow pointer value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this point slow_ptr points to middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine('NULL'); } public static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); Console.Write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); Console.Write ('Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head); } }
// javascript program to delete middle of a linked list class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Function to delete the middle node from the linked list function deleteMid(head) { // If the list is empty return null if (head === null) { return null; } // If the list has only one node delete it and return // null if (head.next === null) { return null; } let prev = null; let slow_ptr = head; let fast_ptr = head; // Move the fast pointer 2 nodes ahead // and the slow pointer 1 node ahead // until the fast pointer reaches the end of the list while (fast_ptr !== null && fast_ptr.next !== null) { fast_ptr = fast_ptr.next.next; // Update prev to hold the previous slow pointer // value prev = slow_ptr; slow_ptr = slow_ptr.next; } // At this point slow_ptr points to the middle node // Bypass the middle node prev.next = slow_ptr.next; // Return the head of the modified list return head; } function printList(head) { let temp = head; while (temp !== null) { process.stdout.write(temp.data + ' -> '); temp = temp.next; } console.log('null'); } // Create a static hardcoded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); process.stdout.write('Original Linked List: '); printList(head); // Delete the middle node head = deleteMid(head); process.stdout.write( 'Linked List after deleting the middle node: '); printList(head);
Izhod
Original Linked List: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL Linked List after deleting the middle node: 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL
Časovna kompleksnost: O (n). Potreben je samo en prehod povezanega seznama
Pomožni prostor: O (1). Ker ni potreben dodatni prostor.
Povezani članek:
- Poiščite sredino povezanega seznama


