Ustvarimo lahko javanski program za razvrščanje elementov niza z uporabo izbirnega razvrščanja. Pri algoritmu razvrščanja izbire iščemo najnižji element in ga razporedimo na ustrezno mesto. Trenutni element zamenjamo z naslednjim najmanjšim številom.
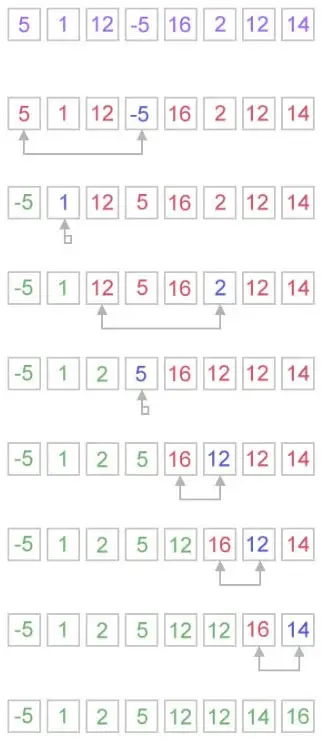
Kako deluje izborno razvrščanje?
Algoritem razvrščanja izbire deluje na zelo preprost način. Za dano matriko vzdržuje dve podmatriki.
odzivna tabela
- Podmatrika je že razvrščena.
- In druga podmatrika je nerazvrščena.
Z vsako ponovitvijo izbirnega razvrščanja je element izbran iz nerazvrščene podmatrike in premaknjen v razvrščeno podmatriko.
čajna žlička proti jedilni žlici
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Časovna zapletenost
najboljše: ?(n^2)Povprečje: ?(n^2)
Najslabše: O(n^2)
Kompleksnost prostora
O(1)Izbira Razvrsti Primer Java
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Razvrščanje izbire v Javi (Drug način)
Uporabite lahko tudi metodo, kjer matrika ni vnaprej določena. Tukaj mora uporabnik vnesti elemente kot vnos.
V naslednjem programu Java prosimo uporabnika, da vnese elemente matrike ali številko, zdaj primerja element matrike in začne zamenjavo s spremenljivko temp. Prvi element postavite v temp in drugi element v prvo, nato pa temp v drugo številko in nadaljujte z naslednjim ujemanjem, da razvrstite celotno matriko v naraščajočem vrstnem redu.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>