Eulerjeva pot je pot v grafu, ki obišče vsak rob točno enkrat. Eulerjev krog je Eulerjeva pot, ki se začne in konča na istem vozlišču.
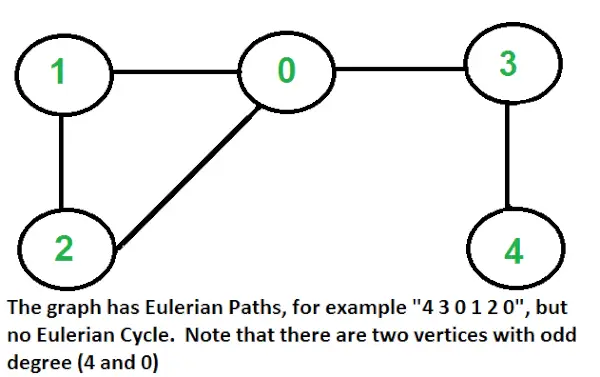


Kako ugotoviti, ali je dani graf Eulerjev ali ne?
Problem je enak naslednjemu vprašanju. Ali je mogoče narisati dani graf, ne da bi dvignili svinčnik s papirja in ne da bi večkrat obrisali kateri koli rob.
Graf se imenuje Eulerjev, če ima Eulerjev cikel, in pol-Eulerjev, če ima Eulerjevo pot. Težava se zdi podobna Hamiltonovi poti, ki je NP popolna težava za splošni graf. Na srečo lahko v polinomskem času ugotovimo, ali ima dani graf Eulerjevo pot ali ne. Pravzaprav ga lahko najdemo v O(V+E) času.
Sledi nekaj zanimivih lastnosti neusmerjenih grafov z Eulerjevo potjo in ciklom. Te lastnosti lahko uporabimo, da ugotovimo, ali je graf Eulerjev ali ne.
Eulerjev cikel: Neusmerjeni graf ima Eulerjev cikel, če sta izpolnjena naslednja dva pogoja.
- Vsa oglišča z različno stopnjo so povezana. Ne zanimajo nas vozlišča z ničelno stopnjo, ker ne pripadajo Eulerjevemu ciklu ali poti (upoštevamo le vse robove).
- Vsa oglišča imajo sodo stopnjo.
Eulerjeva pot: Neusmerjeni graf ima Eulerjevo pot, če sta izpolnjena naslednja dva pogoja.
- Enako kot pogoj (a) za Eulerjev cikel.
- Če ima nič ali dve točki liho stopnjo, vsa druga oglišča pa sodo stopnjo. Upoštevajte, da v neusmerjenem grafu ni možno samo eno vozlišče z liho stopnjo (vsota vseh stopenj je v neusmerjenem grafu vedno soda)
Upoštevajte, da se graf brez robov šteje za Eulerjev, ker ni robov, ki bi jih morali prečkati.
Kako to deluje?
V Eulerjevi poti se vsakič, ko obiščemo vozlišče v, sprehodimo skozi dva neobiskana robova z eno končno točko kot v. Zato morajo imeti vsa srednja oglišča v Eulerjevi poti sodo stopnjo. Za Eulerjev cikel je lahko katero koli oglišče srednje oglišče, zato morajo imeti vsa oglišča sodo stopnjo.
levi spoj proti desnemu spojuPriporočena praksa Eulerjevo vezje in pot Poskusite!
Izvedba:
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A class that represents an undirected graph> class> Graph> {> >int> V;>// No. of vertices> >list<>int>>*adj;>// A dynamic array of adjacency lists> public>:> >// Constructor and destructor> >Graph(>int> V) {>this>->V = V; adj =>new> list<>int>>[IN]; }> >~Graph() {>delete> [] adj; }>// To avoid memory leak> >// function to add an edge to graph> >void> addEdge(>int> v,>int> w);> >// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not> >int> isEulerian();> >// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >bool> isConnected();> >// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();> >void> DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[]);> };> void> Graph::addEdge(>int> v,>int> w)> {> >adj[v].push_back(w);> >adj[w].push_back(v);>// Note: the graph is undirected> }> void> Graph::DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[])> {> >// Mark the current node as visited and print it> >visited[v] =>true>;> >// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >list<>int>>::iterator i;> >for> (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)> >if> (!visited[*i])> >DFSUtil(*i, visited);> }> // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected.> // It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> bool> Graph::isConnected()> {> >// Mark all the vertices as not visited> >bool> visited[V];> >int> i;> >for> (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) vrni false; vrni resnico; } /* Funkcija vrne eno od naslednjih vrednosti 0 --> Če graf ni Eulerjev 1 --> Če ima graf Eulerjevo pot (pol-Eulerjev) 2 --> Če ima graf Eulerjevo vezje (Eulerjevo) */ int Graph::isEulerian() { // Preveri, ali so vsa oglišča brez ničelne stopnje povezana, če (isConnected() == false) vrne 0; // Štetje vozlišč z liho stopnjo int odd = 0; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() & 1) odd++; // Če je štetje več kot 2, potem graf ni Eulerjev, če (odd> 2) vrne 0; // Če je liho štetje je 2, potem je eulerjevo štetje 0, potem je eulerjevo štetje nikoli nemogoče biti 1 za vrnitev neusmerjenega grafa 1 : 2; // Funkcija za izvajanje testnih primerov nična test(Graf &g) { int res = g.isEulerian(); if (res == 0) cout<< 'graph is not Eulerian
'; else if (res == 1) cout << 'graph has a Euler path
'; else cout << 'graph has a Euler cycle
'; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { // Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures Graph g1(5); g1.addEdge(1, 0); g1.addEdge(0, 2); g1.addEdge(2, 1); g1.addEdge(0, 3); g1.addEdge(3, 4); test(g1); Graph g2(5); g2.addEdge(1, 0); g2.addEdge(0, 2); g2.addEdge(2, 1); g2.addEdge(0, 3); g2.addEdge(3, 4); g2.addEdge(4, 0); test(g2); Graph g3(5); g3.addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); test(g3); // Let us create a graph with 3 vertices // connected in the form of cycle Graph g4(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); test(g4); // Let us create a graph with all vertices // with zero degree Graph g5(3); test(g5); return 0; }> |
>
>
pomenska napaka
Java
// A Java program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> import> java.io.*;> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.LinkedList;> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> LinkedList adj[];> >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> LinkedList[v];> >for> (>int> i=>0>; i adj[i] = new LinkedList(); } //Function to add an edge into the graph void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].add(w);// Add w to v's list. adj[w].add(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS void DFSUtil(int v,boolean visited[]) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { int n = i.next(); if (!visited[n]) DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from boolean isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited boolean visited[] = new boolean[V]; int i; for (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) vrni false; vrni resnico; } /* Funkcija vrne eno od naslednjih vrednosti 0 --> Če graf ni Eulerjev 1 --> Če ima graf Eulerjevo pot (pol-Eulerjev) 2 --> Če ima graf Eulerjevo vezje (Eulerjevo) */ int isEulerian() { // Preveri, ali so vsa oglišča brez ničelne stopnje povezana, če (isConnected() == false) vrne 0; // Štetje vozlišč z liho stopnjo int odd = 0; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size()%2!=0) odd++; // Če je število več kot 2, potem graf ni Eulerjev, če (odd> 2) vrne 0; / / Če je liho število 2, potem je liho število 0, potem je liho število nikoli ne more biti 1 za neusmerjeni graf. Funkcija za izvajanje testnih primerov void test() { int res = isEulerian(); if (res == 0) System.out.println('graph is not Eulerian'); else if (res == 1) System. out.println('graf ima Eulerjev cikel'); else System.out.println('graf ima Eulerjev cikel') // Metoda gonilnika public static void main(String args[]); / Ustvarimo in preizkusimo grafe, prikazane na zgornjih slikah Graph g1.addEdge(1, 0); g1.addEdge(2, 1); (0, 3); g1.addEdge (0, 2); Graph g2. addEdge(2, 3); g2.addEdge(4, 0); g3 = new Graph(5). .addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); g3.test(); // Ustvarimo graf s 3 vozlišči // povezanimi v obliki cikla Graph g4 = new Graph(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); g4.test(); // Ustvarimo graf z vsemi vozlišči // z ničelno stopinjo Graph g5 = new Graph(3); g5.test(); } } // To kodo je prispeval Aakash Hasija> |
>
>
Python3
model tcp ip
# Python program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #Complexity : O(V+E)> from> collections>import> defaultdict> # This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation> class> Graph:> >def> __init__(>self>, vertices):> >self>.V>=> vertices># No. of vertices> >self>.graph>=> defaultdict(>list>)># default dictionary to store graph> ># function to add an edge to graph> >def> addEdge(>self>, u, v):> >self>.graph[u].append(v)> >self>.graph[v].append(u)> ># A function used by isConnected> >def> DFSUtil(>self>, v, visited):> ># Mark the current node as visited> >visited[v]>=> True> ># Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >for> i>in> self>.graph[v]:> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False>:> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> >'''Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are> >connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> >node with non-zero degree'''> >def> isConnected(>self>):> ># Mark all the vertices as not visited> >visited>=> [>False>]>*>(>self>.V)> ># Find a vertex with non-zero degree> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i]) !>=> 0>:> >break> ># If there are no edges in the graph, return true> >if> i>=>=> self>.V>->1>:> >return> True> ># Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False> and> len>(>self>.graph[i])>>0>:> >return> False> >return> True> >'''The function returns one of the following values> >0 -->Če graf ni Eulerjev> >1 -->Če ima graf Eulerjevo pot (poleulerjevo)> >2 -->Če ima graf Eulerjevo vezje (Eulerjev) '''> >def> isEulerian(>self>):> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >if> self>.isConnected()>=>=> False>:> >return> 0> >else>:> ># Count vertices with odd degree> >odd>=> 0> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i])>%> 2> !>=> 0>:> >odd>+>=> 1> >'''If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.> >If odd count is 0, then eulerian> >If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian> >Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph'''> >if> odd>=>=> 0>:> >return> 2> >elif> odd>=>=> 2>:> >return> 1> >elif> odd>>2>:> >return> 0> ># Function to run test cases> >def> test(>self>):> >res>=> self>.isEulerian()> >if> res>=>=> 0>:> >print>(>'graph is not Eulerian'>)> >elif> res>=>=> 1>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler path'>)> >else>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler cycle'>)> # Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures> g1>=> Graph(>5>)> g1.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g1.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g1.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g1.test()> g2>=> Graph(>5>)> g2.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g2.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g2.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g2.addEdge(>4>,>0>)> g2.test()> g3>=> Graph(>5>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g3.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g3.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>3>)> g3.test()> # Let us create a graph with 3 vertices> # connected in the form of cycle> g4>=> Graph(>3>)> g4.addEdge(>0>,>1>)> g4.addEdge(>1>,>2>)> g4.addEdge(>2>,>0>)> g4.test()> # Let us create a graph with all vertices> # with zero degree> g5>=> Graph(>3>)> g5.test()> # This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav> |
>
>
C#
kazalec dereference c
// A C# program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> > // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> public> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> > >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> List<>int>>[]adj;> > >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> List<>int>>[in];> >for> (>int> i=0; i adj[i] = new List |
>
>
Javascript
kaj je zemljevid java
> // A Javascript program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class Graph> {> >// Constructor> >constructor(v)> >{> >this>.V = v;> >this>.adj =>new> Array(v);> >for> (let i = 0; i this.adj[i] = []; } // Function to add an edge into the graph addEdge(v,w) { this.adj[v].push(w);// Add w to v's list. this.adj[w].push(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS DFSUtil(v,visited) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex for(let i of this.adj[v]) { let n = i; if (!visited[n]) this.DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited let visited = new Array(this.V); let i; for (i = 0; i |
>
>Izhod
graph has a Euler path graph has a Euler cycle graph is not Eulerian graph has a Euler cycle graph has a Euler cycle>
Časovna zahtevnost: O(V+E)
Kompleksnost prostora: O(V+E)
Naslednji članki:
Eulerjeva pot in vezje za usmerjene grafe.
Fleuryjev algoritem za tiskanje Eulerjeve poti ali vezja?
