Eulerjeva Totientova funkcija Φ(n) za vnos n je število števil v {1, 2, 3, …, n-1}, ki so relativno praštevilna z n, tj. števil, katerih GCD (največji skupni delitelj) z n je 1.
Primeri:
Φ(1) = 1
gcd(1, 1) je 1
Φ(2) = 1
gcd(1, 2) je 1, vendar je gcd(2, 2) 2.
Φ(3) = 2
gcd(1, 3) je 1 in gcd(2, 3) je 1
Φ(4) = 2
gcd(1, 4) je 1 in gcd(3, 4) je 1
Φ(5) = 4
gcd(1, 5) je 1, gcd(2, 5) je 1,
gcd(3, 5) je 1 in gcd(4, 5) je 1
Φ(6) = 2
gcd(1, 6) je 1 in gcd(5, 6) je 1,
Priporočena praksa Funkcija Euler Totient Poskusite!
Kako izračunati Φ(n) za vnos n?
A preprosta rešitev je iteracija skozi vsa števila od 1 do n-1 in štetje števil z gcd z n kot 1. Spodaj je implementacija preproste metode za izračun Eulerjeve funkcije Totient za vhodno celo število n.
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh>Python3 # A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a == 0): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range(2, n): if (gcd(i, n) == 1): result+=1 return result # Driver Code for n in range(1, 11): print('phi(',n,') = ', phi(n), sep = '') # This code is contributed # by Smitha>C# // A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi(int n) { int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for (int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal>Javascript >PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd($a, $b) { if ($a == 0) return $b; return gcd($b % $a, $a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi($n) { $result = 1; for ($i = 2; $i <$n; $i++) if (gcd($i, $n) == 1) $result++; return $result; } // Driver Code for ($n = 1; $n <= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>>C++ // A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd(int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << 'phi('< Izhod
fi(1) = 1 fi(2) = 1 fi(3) = 2 fi(4) = 2 fi(5) = 4 fi(6) = 2 fi(7) = 6 fi(8) = 4 fi( 9) = 6 fi(10) = 4
Zgornja koda pokliče funkcijo gcd O(n)-krat. Časovna kompleksnost funkcije gcd je O(h), kjer je h število števk v manjšem številu danih dveh števil. Zato je zgornja meja na časovna kompleksnost zgornje rešitve je O(N^2 log N) [Kako je Φ lahko največ Log10n števk v vseh številkah od 1 do n]
Pomožni prostor: O(log N)
Spodaj je a Boljša rešitev . Ideja temelji na Eulerjevi formuli produkta, ki pravi, da je vrednost totientnih funkcij pod skupnimi prafaktorji produkta p od n.
Formula v bistvu pravi, da je vrednost Φ(n) enaka n pomnoženemu stranskemu produktu (1 – 1/p) za vse prafaktorje p od n. Na primer vrednost Φ(6) = 6 * (1-1/2) * (1 – 1/3) = 2.
Vse prafaktorje lahko najdemo z uporabo ideje, uporabljene v to post.
1) Inicializiraj: rezultat = n
2) Zaženite zanko od 'p' = 2 do sqrt(n), naredite naslednje za vsak 'p'.
a) Če p deli n, potem
Set: rezultat = rezultat * (1,0 - (1,0 / (float) p));
Razdeli vse pojavitve p v n.
3) Vrni rezultat
Spodaj je implementacija Eulerjeve formule produkta.
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; //Ker so v množici {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n //če je n praštevilo vrni (int)rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika int main() { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) <C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include int phi(int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; //Ker so v množici {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n //če je n praštevilo vrni (int)rezultat; } // Program gonilnika za testiranje nad funkcijo int main() { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; //Ker so v množici {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n //če je n praštevilo vrni (int)rezultat; } // Program gonilnika za testiranje zgornje funkcije public static void main(String args[]) { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari.>Python3 # Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p<= n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p == 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p == 0 : n = n // p result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / float(p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n>1 : rezultat -= rezultat // n #Ker so v nizu {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n #če je n praštevilo vrni int(rezultat) # Gonilnik program za testiranje zgornje funkcije za n v območju (1, 11) : print('phi(', n, ') = ', phi(n)) # To kodo je prispeval # Nikita Tiwari.>C# // C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (float)(1.0 - (1.0 / (float)p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; //Ker so v množici {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n //če je n praštevilo vrni (int)rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika public static void Main() { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal.>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; //Ker so v nizu {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n //če je n praštevilo vrni parseInt(rezultat); } // Koda gonilnika za (naj bo n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi($n) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n /= $p; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $rezultat -= $rezultat / $n; //Ker so v množici {1,2,....,n-1} vsa števila relativno praštevila z n //če je n praštevilo return intval($result); } // Koda gonilnika za ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(' .$n. ') =' . phi($n).'
'; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ>> Izhod
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Časovna zapletenost: O(Φ n log n)
Pomožni prostor: O(1)
Pri zgornji metodi se lahko izognemo izračunom s plavajočo vejico. Ideja je prešteti vse prafaktorje in njihove večkratnike ter to število odšteti od n, da dobimo vrednost funkcije totient (prafaktorji in večkratniki prafaktorjev ne bodo imeli gcd kot 1)
1) Inicializirajte rezultat kot n
2) Upoštevajte vsako število 'p' (kjer se 'p' spreminja od 2 do Φ(n)).
Če p deli n, naredite naslednje
a) Odštejte vse večkratnike p od 1 do n [vse večkratnike p
bo imel gcd več kot 1 (vsaj p) z n]
b) Posodobite n tako, da ga večkrat delite s p.
3) Če je zmanjšani n večji od 1, potem odstranite vse večkratnike
od n iz rezultata.
Spodaj je implementacija zgornjega algoritma.
C++ // C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include using namespace std; int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for(int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; vrni rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika int main() { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) { cout << 'Phi' << '(' << n << ')' << ' = ' << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu>C // C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include int phi(int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; vrni rezultat; } // Program gonilnika za testiranje nad funkcijo int main() { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) printf('phi(%d) = %d
', n, phi(n)); return 0; }>Java // Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; vrni rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika public static void main (String[] args) { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) System.out.println('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit>Python3 # Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2; while(p * p <= n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p == 0): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p == 0): n = int(n / p); result -= int(result / p); p += 1; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n>1): rezultat -= int(rezultat / n); vrni rezultat; # Koda gonilnika za n v območju (1, 11): print('phi(',n,') =', phi(n)); # To kodo prispeva # mits>C# // C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi(int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for (int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= rezultat / n; vrni rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika static public void Main () { int n; za (n = 1; n<= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine('phi(' + n + ') = ' + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit>Javascript // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n>1) rezultat -= parseInt(rezultat / n); vrni rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika za (naj bo n = 1; n<= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} `); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal>PHP <Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi($n) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ($p = 2; $p * $p <= $n; ++$p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ($n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ($n % $p == 0) $n = (int)$n / $p; $result -= (int)$result / $p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ($n>1) $rezultat -= (int)$rezultat / $n; vrni $rezultat; } // Koda gonilnika za ($n = 1; $n<= 10; $n++) echo 'phi(', $n,') =', phi($n), '
'; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ>> Izhod
Phi(1) = 1 Phi(2) = 1 Phi(3) = 2 Phi(4) = 2 Phi(5) = 4 Phi(6) = 2 Phi(7) = 6 Phi(8) = 4 Phi( 9) = 6 Phi(10) = 4
Časovna zapletenost: O(Φ n log n)
Pomožni prostor: O(1)
Vzemimo primer, da bomo razumeli zgornji algoritem.
n = 10.
Inicializacija: rezultat = 10
2 je prafaktor, torej n = n/i = 5, rezultat = 5
3 ni glavni faktor.
Zanka for se ustavi po 3, ker 4*4 ni manjše ali enako
do 10.
Po zanki for je rezultat = 5, n = 5
Ker je n> 1, je rezultat = rezultat - rezultat/n = 4
Nekaj zanimivih lastnosti Eulerjeve Totientove funkcije
1) Za praštevilo p ,
Dokaz :
Primeri:
2) Za dve praštevili a in b
Dokaz :
Primeri:
3) Za praštevilo p ,
Dokaz :
Primeri:
4) Za dve številki a in b
Poseben primer: gcd(a, b) = 1
Primeri:
Poseben primer:
arraylist v Javi
5) Vsota vrednosti vseh deliteljskih funkcij vseh deliteljev n je enaka n.
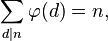
Primeri:
n = 6
dejavniki = {1, 2, 3, 6}
n =
6) Najbolj znana in pomembna lastnost je izražena v Eulerjev izrek :
Izrek pravi, da če sta n in a enako praštevilna
(ali relativno praštevilna) pozitivna cela števila, torej
aΦ(n)Φ 1 (mod n)
The kriptosistem RSA temelji na tem izreku:
V posebnem primeru, ko je m praštevilo, recimo p, se Eulerjev izrek spremeni v t.i Fermatov mali izrek :
ap-1Φ 1 (proti p)
7) Število generatorjev končne ciklične skupine pri seštevanju po modulu n je Φ(n) .
Sorodni članek:
Eulerjeva funkcija Totient za vsa števila, manjša ali enaka n
Optimizirana Eulerjeva totientna funkcija za večkratne ocene
Reference:
http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/
