Zanke v programiranju se uporabljajo za ponavljanje bloka kode, dokler ni izpolnjen podani pogoj. Stavek zanke programerjem omogoča, da večkrat izvedejo stavek ali skupino stavkov brez ponavljanja kode.
spajanje razvrščanje v Javi
C
pretvorba int v niz
// C program to illustrate need of loops> #include> > int> main()> {> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> >printf>(>'Hello World
'>);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Izhod
ddl proti dml
Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World>
V programiranju C obstajata predvsem dve vrsti zank:
- Vstopno nadzorovane zanke: V vstopno nadzorovanih zankah se testni pogoj preveri pred vstopom v glavni del zanke. For Loop in While Loop je Vstopno nadzorovane zanke. Izhodne nadzorovane zanke: V izhodnih nadzorovanih zankah se preskusni pogoj ovrednoti na koncu telesa zanke. Telo zanke se bo izvedlo vsaj enkrat, ne glede na to, ali je pogoj resničen ali napačen. do-while Loop je Izhodna nadzorovana zanka.
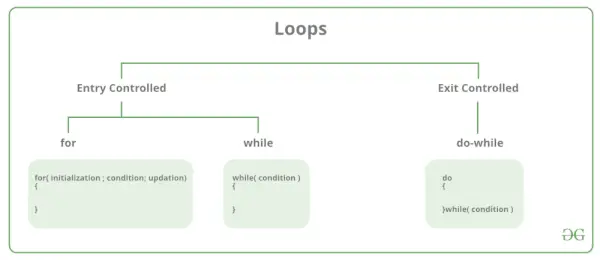
| Vrsta zanke | Opis |
|---|---|
| za zanko | najprej inicializira, nato preveri stanje, nato izvede telo in na koncu je posodobitev končana. |
| medtem ko zanka | najprej inicializira, nato preveri pogoj in nato izvede telo, posodabljanje pa je lahko znotraj telesa. |
| do-while zanka | do-while najprej izvede telo, nato pa se izvede preverjanje pogoja. |
za Loop
for zanka v programiranju C je struktura za nadzor ponavljanja, ki programerjem omogoča pisanje zanke, ki bo izvedena določeno število krat. zanka for programerjem omogoča, da izvedejo n korakov skupaj v eni vrstici.
rezanje jave
Sintaksa:
for (initialize expression; test expression; update expression) { // // body of for loop // }> primer:
for(int i = 0; i In for loop, a loop variable is used to control the loop. Firstly we initialize the loop variable with some value, then check its test condition. If the statement is true then control will move to the body and the body of for loop will be executed. Steps will be repeated till the exit condition becomes true. If the test condition will be false then it will stop. Initialization Expression: In this expression, we assign a loop variable or loop counter to some value. for example: int i=1; Test Expression: In this expression, test conditions are performed. If the condition evaluates to true then the loop body will be executed and then an update of the loop variable is done. If the test expression becomes false then the control will exit from the loop. for example, i<=9; Update Expression: After execution of the loop body loop variable is updated by some value it could be incremented, decremented, multiplied, or divided by any value. for loop Equivalent Flow Diagram: Example: C // C program to illustrate for loop #include // Driver code int main() { int i = 0; for (i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { printf( 'Hello World
'); } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World While Loop While loop does not depend upon the number of iterations. In for loop the number of iterations was previously known to us but in the While loop, the execution is terminated on the basis of the test condition. If the test condition will become false then it will break from the while loop else body will be executed. Syntax: initialization_expression; while (test_expression) { // body of the while loop update_expression; } Flow Diagram for while loop: C // C program to illustrate // while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; // Test expression while(i <10) { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // update expression i++; } return 0; } Output Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World Hello World do-while Loop The do-while loop is similar to a while loop but the only difference lies in the do-while loop test condition which is tested at the end of the body. In the do-while loop, the loop body will execute at least once irrespective of the test condition. Syntax: initialization_expression; do { // body of do-while loop update_expression; } while (test_expression); C // C program to illustrate // do-while loop #include // Driver code int main() { // Initialization expression int i = 2; do { // loop body printf( 'Hello World
'); // Update expression i++; // Test expression } while (i <1); return 0; } Output Hello World Above program will evaluate (i<1) as false since i = 2. But still, as it is a do-while loop the body will be executed once. Loop Control Statements Loop control statements in C programming are used to change execution from its normal sequence. Name Description break statement the break statement is used to terminate the switch and loop statement. It transfers the execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch. continue statement continue statement skips the remainder body and immediately resets its condition before reiterating it. goto statement goto statement transfers the control to the labeled statement. Infinite Loop An infinite loop is executed when the test expression never becomes false and the body of the loop is executed repeatedly. A program is stuck in an Infinite loop when the condition is always true. Mostly this is an error that can be resolved by using Loop Control statements. Using for loop: C // C program to demonstrate infinite // loops using for loop #include // Driver code int main () { int i; // This is an infinite for loop // as the condition expression // is blank for ( ; ; ) { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using While loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { while (1) printf('This loop will run forever.
'); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ... Using the do-while loop: C // C program to demonstrate // infinite loop using do-while // loop #include // Driver code int main() { do { printf('This loop will run forever.
'); } while (1); return 0; } Output This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. This loop will run forever. ...>