Glede na nabor mest in razdaljo med vsakim parom mest je težava najti najkrajšo možno turnejo, ki vsako mesto obišče natanko enkrat in se vrne na izhodišče.
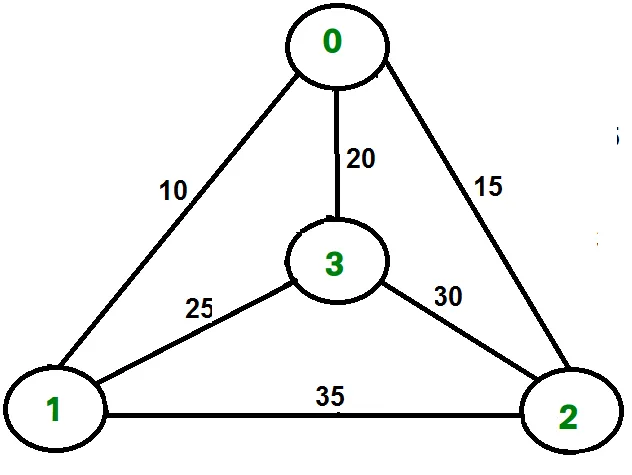
Na primer upoštevajte graf, prikazan na sliki na desni strani. Ogled TSP v grafu je 0-1-3-2-0. Stroški turneje so 10+25+30+15, kar je 80.
Razpravljali smo po rešitvah
1) Naivno in dinamično programiranje
2) Približna rešitev z uporabo MST
Veja in vezana rešitev
Kot je razvidno iz prejšnjih člankov v vejnem in vezanem metodi za trenutno vozlišče v drevesu, izračunamo vezano na najboljšo možno rešitev, ki jo lahko dobimo, če spustimo to vozlišče. Če je vezana na najboljša možna rešitev slabša od trenutne najboljše (najbolje izračunano doslej), potem ignoriramo podrejo, ukoreninjeno z vozliščem.
Upoštevajte, da stroški prek vozlišča vključujejo dva stroška.
1) Stroški doseganja vozlišča iz korena (ko dosežemo vozlišče, imamo izračunane stroške)
2) Stroški doseganja odgovora iz trenutnega vozlišča do lista (izračunamo vezavo na ta strošek, da se odločimo, ali bomo prezrli subtree s tem vozliščem ali ne).
- V primerih a problem maksimizacije Zgornja meja nam pove največjo možno rešitev, če sledimo danemu vozlišču. Na primer v 0/1 Knapsack smo uporabili pohlepni pristop, da smo našli zgornjo mejo .
- V primerih a problem zmanjšanja Spodnja meja nam pove minimalno možno rešitev, če sledimo danemu vozlišču. Na primer v Problem dodelitve zaposlitve Dobimo spodnjo mejo, če delavcu dodelimo najmanj stroškovno delo.
V veji in vezanju je zahtevni del ugotoviti način za izračun vezave na najboljšo možno rešitev. Spodaj je ideja, ki se uporablja za izračun meja za težave s prodajalcem.
Stroški katere koli turneje lahko zapišete kot spodaj.
Cost of a tour T = (1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two edges adjacent to u and in the tour T) where u ? V For every vertex u if we consider two edges through it in T and sum their costs. The overall sum for all vertices would be twice of cost of tour T (We have considered every edge twice.) (Sum of two tour edges adjacent to u) >= (sum of minimum weight two edges adjacent to u) Cost of any tour >= 1/2) * ? (Sum of cost of two minimum weight edges adjacent to u) where u ? V
Na primer upoštevajte zgornji prikazani graf. Spodaj sta najnižja stara dva roba ob vsakem vozlišču.
Node Least cost edges Total cost 0 (0 1) (0 2) 25 1 (0 1) (1 3) 35 2 (0 2) (2 3) 45 3 (0 3) (1 3) 45 Thus a lower bound on the cost of any tour = 1/2(25 + 35 + 45 + 45) = 75 Refer this for one more example.
Zdaj imamo idejo o izračunu spodnje meje. Poglejmo, kako uporabiti drevo za iskanje prostora. Začnemo naštevati vsa možna vozlišča (po možnosti v leksikografskem vrstnem redu)
1. koreninsko vozlišče: Brez izgube splošnosti predvidevamo, da začnemo pri Vertex '0', za katero je bila zgoraj izračunana spodnja meja.
Ukvarjanje s stopnjo 2: Naslednja stopnja našteva vse možne točke, na katere se lahko odpravimo (ne pozabite, da se mora na kateri koli poti zgoditi samo enkrat), ki so 1 2 3 ... n (upoštevajte, da je graf končan). Upoštevajte, da izračunamo za Vertex 1, saj smo se preselili z 0 na 1, naša turneja je zdaj vključevala rob 0-1. To nam omogoča, da spremenimo potrebne spremembe v spodnji meji korena.
Lower Bound for vertex 1 = Old lower bound - ((minimum edge cost of 0 + minimum edge cost of 1) / 2) + (edge cost 0-1)
Kako deluje? Če vključimo rob 0-1, dodamo robne stroške 0-1 in odštejemo robovo težo, tako da spodnja meja ostane čim bolj tesna, kar bi bila vsota minimalnih robov 0 in 1, deljena z 2.. Jasno, da rob odšteje ne more biti manjši od tega.
Ukvarjanje z drugimi stopnjami: Ko gremo na naslednjo stopnjo, ponovno naštejemo vse možne točke. Za zgornji primer, ki gre naprej po 1, preverimo za 2 3 4 ... n.
Razmislite o spodnji meji za 2, ko smo se premikali z 1 na 1, vključimo rob 1-2 na ogled in spremenimo novo spodnjo mejo za to vozlišče.
Lower bound(2) = Old lower bound - ((second minimum edge cost of 1 + minimum edge cost of 2)/2) + edge cost 1-2)
OPOMBA: Edina sprememba formule je, da smo tokrat vključili drugi minimalni rob za 1, ker so bili najmanjši stroški roba že odšteti v prejšnji ravni.
// C++ program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. #include
// Java program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. import java.util.*; class GFG { static int N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int final_path[] = new int[N + 1]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static boolean visited[] = new boolean[N]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal(int curr_path[]) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin(int adj[][] int i) { int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) if (adj[i][k] < min && i != k) min = adj[i][k]; return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin(int adj[][] int i) { int first = Integer.MAX_VALUE second = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int j=0; j<N; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (adj[i][j] <= first) { second = first; first = adj[i][j]; } else if (adj[i][j] <= second && adj[i][j] != first) second = adj[i][j]; } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec(int adj[][] int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int curr_path[]) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] != 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level-1]][curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal(curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if (adj[curr_path[level-1]][i] != 0 && visited[i] == false) { int temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res) { curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level-1]][i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array Arrays.fill(visitedfalse); for (int j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP(int adj[][]) { int curr_path[] = new int[N + 1]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0; Arrays.fill(curr_path -1); Arrays.fill(visited false); // Compute initial bound for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = (curr_bound==1)? curr_bound/2 + 1 : curr_bound/2; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { //Adjacency matrix for the given graph int adj[][] = {{0 10 15 20} {10 0 35 25} {15 35 0 30} {20 25 30 0} }; TSP(adj); System.out.printf('Minimum cost : %dn' final_res); System.out.printf('Path Taken : '); for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { System.out.printf('%d ' final_path[i]); } } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
# Python3 program to solve # Traveling Salesman Problem using # Branch and Bound. import math maxsize = float('inf') # Function to copy temporary solution # to the final solution def copyToFinal(curr_path): final_path[:N + 1] = curr_path[:] final_path[N] = curr_path[0] # Function to find the minimum edge cost # having an end at the vertex i def firstMin(adj i): min = maxsize for k in range(N): if adj[i][k] < min and i != k: min = adj[i][k] return min # function to find the second minimum edge # cost having an end at the vertex i def secondMin(adj i): first second = maxsize maxsize for j in range(N): if i == j: continue if adj[i][j] <= first: second = first first = adj[i][j] elif(adj[i][j] <= second and adj[i][j] != first): second = adj[i][j] return second # function that takes as arguments: # curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node # curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far # level-> current level while moving # in the search space tree # curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored # which would later be copied to final_path[] def TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path visited): global final_res # base case is when we have reached level N # which means we have covered all the nodes once if level == N: # check if there is an edge from # last vertex in path back to the first vertex if adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] != 0: # curr_res has the total weight # of the solution we got curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1]] [curr_path[0]] if curr_res < final_res: copyToFinal(curr_path) final_res = curr_res return # for any other level iterate for all vertices # to build the search space tree recursively for i in range(N): # Consider next vertex if it is not same # (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and # not visited already) if (adj[curr_path[level-1]][i] != 0 and visited[i] == False): temp = curr_bound curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] # different computation of curr_bound # for level 2 from the other levels if level == 1: curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2) else: curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2) # curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound # for the node that we have arrived on. # If current lower bound < final_res # we need to explore the node further if curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res: curr_path[level] = i visited[i] = True # call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path visited) # Else we have to prune the node by resetting # all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] curr_bound = temp # Also reset the visited array visited = [False] * len(visited) for j in range(level): if curr_path[j] != -1: visited[curr_path[j]] = True # This function sets up final_path def TSP(adj): # Calculate initial lower bound for the root node # using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + # second min) for all edges. Also initialize the # curr_path and visited array curr_bound = 0 curr_path = [-1] * (N + 1) visited = [False] * N # Compute initial bound for i in range(N): curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)) # Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = math.ceil(curr_bound / 2) # We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex # in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = True curr_path[0] = 0 # Call to TSPRec for curr_weight # equal to 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path visited) # Driver code # Adjacency matrix for the given graph adj = [[0 10 15 20] [10 0 35 25] [15 35 0 30] [20 25 30 0]] N = 4 # final_path[] stores the final solution # i.e. the // path of the salesman. final_path = [None] * (N + 1) # visited[] keeps track of the already # visited nodes in a particular path visited = [False] * N # Stores the final minimum weight # of shortest tour. final_res = maxsize TSP(adj) print('Minimum cost :' final_res) print('Path Taken : ' end = ' ') for i in range(N + 1): print(final_path[i] end = ' ') # This code is contributed by ng24_7
// C# program to solve Traveling Salesman Problem // using Branch and Bound. using System; public class GFG { static int N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. static int[] final_path = new int[N + 1]; // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path static bool[] visited = new bool[N]; // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. static int final_res = Int32.MaxValue; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution static void copyToFinal(int[] curr_path) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int firstMin(int[ ] adj int i) { int min = Int32.MaxValue; for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) if (adj[i k] < min && i != k) min = adj[i k]; return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i static int secondMin(int[ ] adj int i) { int first = Int32.MaxValue second = Int32.MaxValue; for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { if (i == j) continue; if (adj[i j] <= first) { second = first; first = adj[i j]; } else if (adj[i j] <= second && adj[i j] != first) second = adj[i j]; } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored // which // would later be copied to final_path[] static void TSPRec(int[ ] adj int curr_bound int curr_weight int level int[] curr_path) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1] curr_path[0]] != 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got int curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1] curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal(curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { // Consider next vertex if it is not same // (diagonal entry in adjacency matrix and not // visited already) if (adj[curr_path[level - 1] i] != 0 && visited[i] == false) { int temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1] i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level == 1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin(adj i)) / 2); // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual // lower bound for the node that we have // arrived on If current lower bound < // final_res we need to explore the node // further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res) { curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec(adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by // resetting all changes to curr_weight and // curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1] i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array Array.Fill(visited false); for (int j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] static void TSP(int[ ] adj) { int[] curr_path = new int[N + 1]; // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array int curr_bound = 0; Array.Fill(curr_path -1); Array.Fill(visited false); // Compute initial bound for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) curr_bound += (firstMin(adj i) + secondMin(adj i)); // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = (curr_bound == 1) ? curr_bound / 2 + 1 : curr_bound / 2; // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec(adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } // Driver code static public void Main() { // Adjacency matrix for the given graph int[ ] adj = { { 0 10 15 20 } { 10 0 35 25 } { 15 35 0 30 } { 20 25 30 0 } }; TSP(adj); Console.WriteLine('Minimum cost : ' + final_res); Console.Write('Path Taken : '); for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { Console.Write(final_path[i] + ' '); } } } // This code is contributed by Rohit Pradhan
const N = 4; // final_path[] stores the final solution ie the // path of the salesman. let final_path = Array (N + 1).fill (-1); // visited[] keeps track of the already visited nodes // in a particular path let visited = Array (N).fill (false); // Stores the final minimum weight of shortest tour. let final_res = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; // Function to copy temporary solution to // the final solution function copyToFinal (curr_path){ for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ final_path[i] = curr_path[i]; } final_path[N] = curr_path[0]; } // Function to find the minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function firstMin (adj i){ let min = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let k = 0; k < N; k++){ if (adj[i][k] < min && i !== k){ min = adj[i][k]; } } return min; } // function to find the second minimum edge cost // having an end at the vertex i function secondMin (adj i){ let first = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; let second = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for (let j = 0; j < N; j++){ if (i == j){ continue; } if (adj[i][j] <= first){ second = first; first = adj[i][j]; } else if (adj[i][j] <= second && adj[i][j] !== first){ second = adj[i][j]; } } return second; } // function that takes as arguments: // curr_bound -> lower bound of the root node // curr_weight-> stores the weight of the path so far // level-> current level while moving in the search // space tree // curr_path[] -> where the solution is being stored which // would later be copied to final_path[] function TSPRec (adj curr_bound curr_weight level curr_path) { // base case is when we have reached level N which // means we have covered all the nodes once if (level == N) { // check if there is an edge from last vertex in // path back to the first vertex if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]] !== 0) { // curr_res has the total weight of the // solution we got let curr_res = curr_weight + adj[curr_path[level - 1]][curr_path[0]]; // Update final result and final path if // current result is better. if (curr_res < final_res) { copyToFinal (curr_path); final_res = curr_res; } } return; } // for any other level iterate for all vertices to // build the search space tree recursively for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ // Consider next vertex if it is not same (diagonal // entry in adjacency matrix and not visited // already) if (adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i] !== 0 && !visited[i]){ let temp = curr_bound; curr_weight += adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; // different computation of curr_bound for // level 2 from the other levels if (level == 1){ curr_bound -= (firstMin (adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin (adj i)) / 2; } else { curr_bound -= (secondMin (adj curr_path[level - 1]) + firstMin (adj i)) / 2; } // curr_bound + curr_weight is the actual lower bound // for the node that we have arrived on // If current lower bound < final_res we need to explore // the node further if (curr_bound + curr_weight < final_res){ curr_path[level] = i; visited[i] = true; // call TSPRec for the next level TSPRec (adj curr_bound curr_weight level + 1 curr_path); } // Else we have to prune the node by resetting // all changes to curr_weight and curr_bound curr_weight -= adj[curr_path[level - 1]][i]; curr_bound = temp; // Also reset the visited array visited.fill (false) for (var j = 0; j <= level - 1; j++) visited[curr_path[j]] = true; } } } // This function sets up final_path[] function TSP (adj) { let curr_path = Array (N + 1).fill (-1); // Calculate initial lower bound for the root node // using the formula 1/2 * (sum of first min + // second min) for all edges. // Also initialize the curr_path and visited array let curr_bound = 0; visited.fill (false); // compute initial bound for (let i = 0; i < N; i++){ curr_bound += firstMin (adj i) + secondMin (adj i); } // Rounding off the lower bound to an integer curr_bound = curr_bound == 1 ? (curr_bound / 2) + 1 : (curr_bound / 2); // We start at vertex 1 so the first vertex // in curr_path[] is 0 visited[0] = true; curr_path[0] = 0; // Call to TSPRec for curr_weight equal to // 0 and level 1 TSPRec (adj curr_bound 0 1 curr_path); } //Adjacency matrix for the given graph let adj =[[0 10 15 20] [10 0 35 25] [15 35 0 30] [20 25 30 0]]; TSP (adj); console.log (`Minimum cost:${final_res}`); console.log (`Path Taken:${final_path.join (' ')}`); // This code is contributed by anskalyan3.
Izhod:
Minimum cost : 80 Path Taken : 0 1 3 2 0
Zaokroževanje se izvaja v tej vrstici kode:
if (level==1) curr_bound -= ((firstMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2); else curr_bound -= ((secondMin(adj curr_path[level-1]) + firstMin(adj i))/2);
V algoritmu podružnice in vezanega TSP izračunamo spodnjo mejo skupnih stroškov optimalne rešitve, tako da dodamo minimalne stroške roba za vsako točko in nato delimo z dvema. Vendar ta spodnja meja morda ni celo število. Če želite dobiti celotno spodnjo mejo, lahko uporabimo zaokroževanje.
V zgornji kodi spremenljivka Curr_Bound vsebuje trenutno spodnjo mejo skupnih stroškov optimalne rešitve. Ko obiščemo novo točko na ravni, izračunamo novo spodnjo mejo new_bound, tako da vzamemo vsoto najmanjših stroškov roba za novo vrhovo in njena dva najbližja soseda. Nato posodobimo spremenljivko Curr_bound tako, da zaokrožimo novo_bound do najbližjega števila.
Če je raven 1, zaokrožimo do najbližjega števila. To je zato, ker smo doslej obiskali samo eno točko in želimo biti konzervativni pri oceni skupnih stroškov optimalne rešitve. Če je raven večja od 1, uporabljamo bolj agresivno strategijo zaokroževanja, ki upošteva dejstvo, da smo že obiskali nekatere točke in lahko zato natančneje ocenimo skupne stroške optimalne rešitve.
Časovna kompleksnost: Najslabša kompleksnost veje in vezanja ostaja enaka kot v surovi sili, ker v najslabšem primeru nikoli ne bomo imeli možnosti za obrezovanje vozlišča. Ker v praksi deluje zelo dobro, odvisno od različnih primerkov TSP. Kompleksnost je odvisna tudi od izbire mejne funkcije, saj so tiste, ki odločajo, koliko vozlišč je treba obrezati.
Reference:
http://lcm.csa.iisc.ernet.in/dsa/node187.html
