Podan je pravokoten papir dimenzij a x b . Naloga je razrezati celoten papir na najmanj število kvadrat kosov. Izberemo lahko kvadratne kose poljubne velikosti, vendar morajo biti razrezani brez prekrivanja ali puščanja dodatnega prostora .
Primeri:
Vnos: a = 5 b = 8
5 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 5 X 8
Izhod: 5
Pojasnilo: Papir lahko razrežemo na 5 kvadratov: 1 kvadrat velikosti 5x5 1 kvadrat velikosti 3x3 1 kvadrat velikosti 2x2 in 2 kvadrata velikosti 1x1.Vnos: a = 13 b = 11
6 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 13 X 11
Izhod: 6
Pojasnilo: Papir lahko razrežemo na 6 kvadratov: 1 kvadrat velikosti 7x7 1 kvadrat velikosti 6x6 1 kvadrat velikosti 5x5 2 kvadrata velikosti 4x4 in 1 kvadrat velikosti 1x1.niz predolgVnos: a = 6 b = 7
5 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 6 X 7
Izhod: 5
Pojasnilo: Papir lahko razrežemo na 5 kvadratov: 1 kvadrat velikosti 4x4, 2 kvadrata velikosti 3x3 in 2 kvadrata velikosti 3x3.
Kazalo vsebine
- [Nepravilen pristop 1] Uporaba pohlepne tehnike
- [Nepravilen pristop 2] Uporaba dinamičnega programiranja
- [Pravilni pristop] Uporaba DFS in dinamičnega programiranja
[Nepravilen pristop 1] Uporaba pohlepne tehnike
Na prvi pogled se morda zdi, da težavo enostavno rešimo tako, da najprej iz papirja izrežemo čim večji kvadrat, nato pa iz preostalega papirja izrežemo največji kvadrat in tako naprej, dokler ne izrežemo celotnega papirja. Toda ta rešitev je napačna.
Zakaj Greedy Approach ne deluje?
delna odvisnostRazmislite o velikosti papirja 6x7 potem, če poskušamo pohlepno rezati papir, bomo dobili 7 kvadrati: 1 kvadrat velikosti 6x6 in 6 kvadratov velikosti 1x1 medtem ko je pravilna rešitev: 5. Zato pohlepen pristop ne bo deloval.
[Nepravilen pristop 2] Uporaba dinamičnega programiranja
Dinamično programiranje z navpičnimi ali vodoravnimi rezi: Druga rešitev, ki se morda zdi pravilna, je uporaba Dinamično programiranje . Tabelo dp[][] lahko vzdržujemo tako, da dp[i][j] = najmanjše število kvadratov, ki jih je mogoče izrezati iz papirja velikosti i x j . Nato za papir velikosti axb
- Lahko ga poskusimo razrezati vzdolž vsake vrstice: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) kjer je k lahko v območju [1 i - 1].
- Lahko ga poskusimo razrezati vzdolž vsakega stolpca: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) kjer je k lahko v območju [1 j - 1].
Končno bo odgovor najmanj vseh rezov. Toda tudi ta rešitev je napačna.
Zakaj navpično ali vodoravno rezanje s pristopom dinamičnega programiranja ne deluje?
To ne bo delovalo, ker predpostavljamo, da bo navpični ali vodoravni rez vedno razdelil pravokotnik na dva dela. Razmislite o velikosti papirja 13x11 potem, če poskušamo rezati papir s pristopom DP, bomo dobili 8 kvadratov, vendar je pravilen odgovor (kot je prikazano v primerih) 6. Zato dinamično programiranje ne bo delovalo.
[Pravilni pristop] Uporaba DFS in dinamičnega programiranja
C++The ideja je izrezati celoten papir z uporabo DFS v od spodaj navzgor način. V vsakem koraku poiščite najnižji levi kot papirja in poskusite iz tega vogala izrezati kvadrate vseh možnih velikosti. Ko ponovno izrežete kvadrat, poiščite najnižji levi kot preostalega papirja, da izrežete kvadrate vseh možnih velikosti in tako naprej. Toda če poskusimo vse možne reze iz najnižjega levega vogala vseh možnih velikosti papirja, potem bi bilo precej neučinkovito. Optimiziramo ga lahko z uporabo Dinamično programiranje za shranjevanje najmanjših kosov za vsako možno velikost papirja.
Za enolično identifikacijo katere koli velikosti papirja lahko vzdržujemo matriko remSq[] tako, da remSq[i] shrani število preostalih kvadratov velikosti 1x1 v i-ti stolpec papirja. Torej za papir velikosti 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Tudi za iskanje najnižjega levega kota bomo našli prvi indeks z največ preostalimi kvadratki. Tako lahko zgostimo vrednost matrike remSq[], da poiščemo edinstven ključ za vse možne vrednosti matrike remSq[].
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Izhod
6
Časovna zahtevnost: O(a^b) za vsakega od b stolpcev imamo lahko kvadratke.
Pomožni prostor: O(a^b) zaradi memoizacije, ki shrani vsako edinstveno stanje.

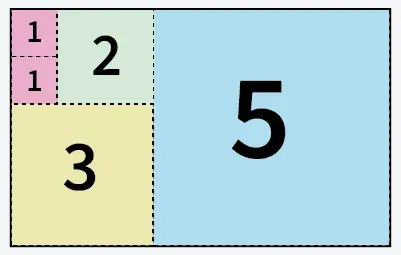 5 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 5 X 8
5 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 5 X 8 6 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 13 X 11
6 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 13 X 11 5 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 6 X 7
5 kvadratov, izrezanih iz papirja velikosti 6 X 7