Minimax je nekakšen algoritem za sledenje nazaj, ki se uporablja pri odločanju in teoriji iger za iskanje optimalne poteze za igralca ob predpostavki, da tudi vaš nasprotnik igra optimalno. Pogosto se uporablja v poteznih igrah za dva igralca, kot so Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, Šah itd.
V Minimaxu se dva igralca imenujeta maksimizer in minimizer. The maksimizator poskuša doseči najvišjo možno oceno, medtem ko minimizator poskuša narediti nasprotno in dobiti najnižjo možno oceno.
Vsako stanje plošče ima z njim povezano vrednost. V danem stanju, če ima maksimizator prednost, bo rezultat deske ponavadi pozitivna vrednost. Če ima minimizator prednost v tem stanju plošče, bo to ponavadi negativna vrednost. Vrednosti plošče so izračunane z nekaterimi hevristikami, ki so edinstvene za vsako vrsto igre.
primer:
Razmislite o igri, ki ima 4 končna stanja in poti do končnega stanja so od korena do 4 listov popolnega binarnega drevesa, kot je prikazano spodaj. Predpostavimo, da ste maksimizirajoči igralec in imate prvo priložnost za premik, tj. ste na osnovni ravni, vaš nasprotnik pa na naslednji stopnji. Katero potezo bi naredili kot maksimizirajoči igralec glede na to, da tudi vaš nasprotnik igra optimalno?
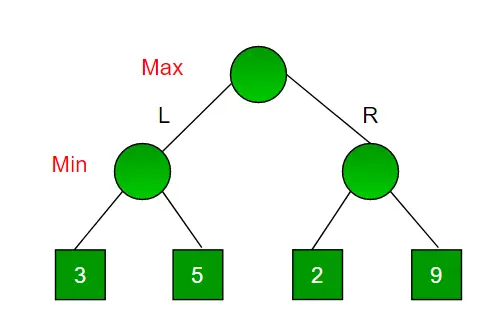
Ker je to algoritem, ki temelji na sledenju nazaj, poskusi vse možne poteze, nato se vrne nazaj in sprejme odločitev.
- Maksimizator gre LEVO: Zdaj so na vrsti minimizatorji. Minimizator ima zdaj izbiro med 3 in 5. Ker je minimizator, bo zagotovo izbral najmanj med obema, to je 3
- Maksimizator gre PRAV: Zdaj so na vrsti minimizatorji. Minimizator ima zdaj možnost izbire med 2 in 9. Izbral bo 2, saj je najmanjša med obema vrednostma.
Kot maksimizator bi izbrali večjo vrednost, ki je 3. Zato je optimalna poteza za maksimizator, da gre LEVO, optimalna vrednost pa je 3.
Zdaj je drevo igre videti takole:

Zgornje drevo prikazuje dva možna rezultata, ko se maksimizator premakne levo in desno.
Opomba: Čeprav je na desnem poddrevesu vrednost 9, minimizator tega ne bo nikoli izbral. Vedno moramo predvidevati, da naš nasprotnik igra optimalno.
Spodaj je izvedba za isto.
C++
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
>
C#
jdbc jdbc
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
>
>
Python3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
Javascript
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
>
Izhod:
The optimal value is: 12>
Časovna zahtevnost: O(b^d) b je faktor razvejanja in d je štetje globine ali plasti grafa ali drevesa.
Kompleksnost prostora: O(bd), kjer je b faktor razvejanja v d, je največja globina drevesa, podobna DFS.
Ideja tega članka je predstaviti Minimax s preprostim primerom.
- V zgornjem primeru sta za igralca samo dve možnosti. Na splošno je izbire lahko več. V tem primeru se moramo ponoviti za vse možne poteze in najti maksimum/minimum. Na primer, v igri Tic-Tac-Toe lahko prvi igralec naredi 9 možnih potez.
- V zgornjem primeru so nam dani rezultati (listi Game Tree). Za tipično igro moramo izpeljati te vrednosti
Kmalu bomo pokrivali Tic Tac Toe z algoritmom Minimax.
Ta članek je prispeval Akshay L. Aradhya.
