Glede na dva niza, S1 in S2 , naloga je najti dolžino najdaljšega skupnega podzaporedja, tj. najdaljšega podzaporedja, ki je prisotno v obeh nizih.
A najdaljše skupno podzaporedje (LCS) je definiran kot najdaljše podzaporedje, ki je skupno v vseh danih vhodnih zaporedjih.
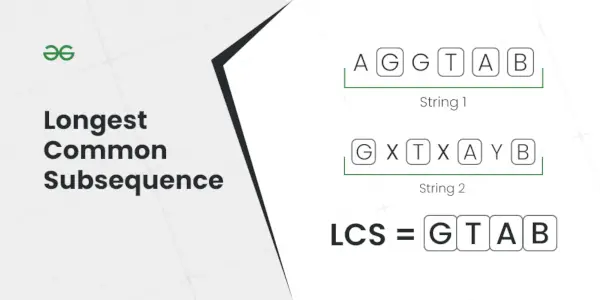
Najdaljše skupno podzaporedje
Primeri:
pisava gimp
Priporočena praksa Najdaljše skupno zaporedje Poskusite!Vnos: S1 = ABC, S2 = ACD
Izhod: 2
Pojasnilo: Najdaljše podzaporedje, ki je prisotno v obeh nizih, je AC.Vnos: S1 = AGGTAB, S2 = GXTXAYB
Izhod: 4
Pojasnilo: Najdaljše skupno podzaporedje je GTAB.Vnos: S1 = ABC, S2 = CBA
Izhod: 1
Pojasnilo: Obstajajo tri pogosta podzaporedja dolžine 1, A, B in C in nobeno skupno podzaporedje dolžine več kot 1.Vnos: S1 = XYZW, S2 = XYWZ
Izhod: 3
Pojasnilo: Obstajata dve pogosti podzaporedji dolžine 3 XYZ in XYW, skupnega podzaporedja pa ni. dolžine več kot 3.
Najdaljše skupno podzaporedje (LCS) z uporabo rekurzije:
Generirajte vsa možna podzaporedja in z uporabo poiščite najdaljše med njimi, ki je prisotno v obeh nizih Za uresničitev ideje sledite spodnjim korakom:
- Ustvarite rekurzivno funkcijo [recimo lcs() ].
- Preverite razmerje med prvimi znaki nizov, ki še niso obdelani.
- Glede na relacijo pokličite naslednjo rekurzivno funkcijo, kot je navedeno zgoraj.
- Vrne dolžino LCS, prejetega kot odgovor.
Spodaj je implementacija rekurzivnega pristopa:
C++C// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra>Java// A Naive recursive implementation // of LCS problem #include int max(int a, int b); // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int i, int j) // Utility function to get max of // 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Koda gonilnika int main() { char S1[] = 'BD'; char S2[] = 'ABCD'; int m = strlen(S1); int n = strlen(S2); int i = 0, j = 0; // Klic funkcije printf('Dolžina LCS je %d', lcs(S1, S2, i, j)); vrni 0; }>Python// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem in java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) n == 0) return 0; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1); else return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n)); // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Koda gonilnika public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Niz S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Niz S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.length(); int n = S2.length(); System.out.println('Dolžina LCS je' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // To kodo je prispeval Saket Kumar>C## A Naive recursive Python implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): if m == 0 or n == 0: return 0 elif X[m-1] == Y[n-1]: return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1) else: return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n)) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, len(S1), len(S2)))>Javascript// C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) if (m == 0 // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Koda gonilnika public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Niz S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Dolžina; int n = S2.Dolžina; Console.Write('Dolžina LCS je' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // To kodo je prispeval Sam007>PHP>
IzhodLength of LCS is 4>Časovna zapletenost: O(2m+n)
Pomožni prostor: O(1)Uporaba najdaljšega skupnega podzaporedja (LCS). Memoizacija :
Če natančno opazimo, lahko opazimo, da ima zgornja rekurzivna rešitev naslednji dve lastnosti:
1. Optimalna podkonstrukcija:
Glej za reševanje strukture L(X[0, 1, . . ., m-1], Y [0, 1, . . . , n-1]) si pomagamo s podstrukturami X[0 , 1, …, m-2], Y[0, 1,…, n-2], odvisno od situacije (tj. z njihovo optimalno uporabo) za iskanje rešitve celote.
2. Prekrivajoči se podproblemi:
Če uporabimo zgornji rekurzivni pristop za nize BD in ABCD , bomo dobili delno rekurzijsko drevo, kot je prikazano spodaj. Tukaj lahko vidimo, da se podproblem L(BD, ABCD) izračunava več kot enkrat. Če upoštevamo celotno drevo, bo več takšnih prekrivajočih se podproblemov.
L(AXYT, AYZX)
/
L(AXY, AYZX) L(AXYT, AYZ)
/ /
L(AX, AYZX) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXYT, AY)Pristop: Zaradi prisotnosti teh dveh lastnosti lahko za rešitev problema uporabimo dinamično programiranje ali memoizacijo. Spodaj je pristop k rešitvi z uporabo rekurzije.
- Ustvarite rekurzivno funkcijo. Ustvarite tudi 2D matriko za shranjevanje rezultata edinstvenega stanja.
- Če med klicem rekurzije isto stanje kličemo več kot enkrat, lahko neposredno vrnemo odgovor, shranjen za to stanje, namesto da ponovno izračunamo.
Spodaj je izvedba zgornjega pristopa:
C++Java// A Top-Down DP implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int m, int n, vector>& dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) vrni 0; če (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) vrni dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } vrni dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } // Koda gonilnika int main() { char X[] = 'AGGTAB'; char Y[] = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = strlen(X); int n = strlen(Y); vektor > dp(m + 1, vektor (n + 1, -1)); cout<< 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp); return 0; }> Python/*package whatever //do not write package name here */ import java.io.*; class GFG { // A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n, int[][] dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (dp[m][n] != -1) return dp[m][n]; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) { dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); return dp[m][n]; } dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); return dp[m][n]; } // Drivers code public static void main(String args[]) { String X = 'AGGTAB'; String Y = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = X.length(); int n = Y.length(); int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) { dp[i][j] = -1; } } System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); } } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>C## A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem # Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] def lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp): if (m == 0 or n == 0): return 0 if (dp[m][n] != -1): return dp[m][n] if X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]: dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp) return dp[m][n] dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)) return dp[m][n] # Driver code X = 'AGGTAB' Y = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(X) n = len(Y) dp = [[-1 for i in range(n + 1)]for j in range(m + 1)] print(f'Length of LCS is {lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)}') # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>Javascript/* C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem */ using System; class GFG { /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ static int lcs(char[] X, char[] Y, int m, int n, int[, ] L) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (L[m, n] != -1) return L[m, n]; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) { L[m, n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, L); return L[m, n]; } L[m, n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, L), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, L)); return L[m, n]; } /* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */ static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } public static void Main() { String s1 = 'AGGTAB'; Niz s2 = 'GXTXAYB'; char[] X = s1.ToCharArray(); char[] Y = s2.ToCharArray(); int m = X.Dolžina; int n = Y.Dolžina; int[,] L = novo int[m + 1, n + 1]; za (int i = 0; i<= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { L[i, j] = -1; } } Console.Write('Length of LCS is' + ' ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, L)); } } // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>/* A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem */ /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ function lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) return dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } /* Driver code */ let X = 'AGGTAB'; let Y = 'GXTXAYB'; let m = X.length; let n = Y.length; let dp = new Array(m + 1); for(let i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { dp[i] = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1); } console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>
IzhodLength of LCS is 4>Časovna zapletenost: O(m * n), kjer sta m in n dolžini niza.
Pomožni prostor: O(m * n) Tukaj je rekurzivni skladni prostor prezrt.Najdaljše skupno podzaporedje (LCS) z uporabo od spodaj navzgor (Tabelacija):
Za implementacijo pristopa dinamičnega programiranja za LCS lahko uporabimo naslednje korake.
- Ustvarite 2D niz dp[][] z vrsticami in stolpci, ki so enaki dolžini vsakega vhodnega niza plus 1 [število vrstic označuje indekse S1 stolpci pa označujejo indekse S2 ].
- Inicializirajte prvo vrstico in stolpec matrike dp na 0.
- Iterirajte po vrsticah matrike dp, začenši od 1 (recimo z uporabo iteratorja jaz ).
- Za vsakogar jaz , ponovite vse stolpce iz j = 1 do n :
- če S1[i-1] je enako S2[j-1] , nastavite trenutni element matrike dp na vrednost elementa ( dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 ).
- V nasprotnem primeru nastavite trenutni element matrike dp na največjo vrednost dp[i-1][j] in dp[i][j-1] .
- Za ugnezdenimi zankami bo zadnji element matrike dp vseboval dolžino LCS.
Za boljše razumevanje si oglejte spodnjo sliko:
Ilustracija:
Recite, da so strune S1 = AGGTAB in S2 = GXTXAYB .
Prvi korak: Na začetku ustvarite 2D matriko (recimo dp[][]) velikosti 8 x 7, katere prva vrstica in prvi stolpec sta zapolnjena z 0.
python os listdirUstvarjanje tabele dp
Drugi korak: Premik za i = 1. Ko j postane 5, sta S1[0] in S2[4] enaka. Torej je dp[][] posodobljen. Za druge elemente vzemite največ dp[i-1][j] in dp[i][j-1]. (V tem primeru, če sta obe vrednosti enaki, smo uporabili puščice na prejšnje vrstice).
Polnjenje vrstice št. 1
Tretji korak: Med prečkanjem za i = 2 sta S1[1] in S2[0] enaka (oba sta 'G'). Torej je vrednost dp v tej celici posodobljena. Ostali elementi se posodobijo v skladu s pogoji.
Polnjenje vrstice št. 2
Četrti korak: Za i = 3 sta S1[2] in S2[0] spet enaka. Posodobitve so naslednje.
Vrstica za polnjenje št. 3
Peti korak: Za i = 4 lahko vidimo, da sta S1[3] in S2[2] enaka. Torej dp[4][3] posodobljen kot dp[3][2] + 1 = 2.
Vrstica za polnjenje 4
Šesti korak: Tukaj lahko vidimo, da sta za i = 5 in j = 5 vrednosti S1[4] in S2[4] enaki (tj. obe sta 'A'). Tako se dp[5][5] ustrezno posodobi in postane 3.
brezplačno proti brezplačnimPolnjenje vrstice 5
Zadnji korak: Za i = 6 glejte, da so zadnji znaki obeh nizov enaki (so 'B'). Zato vrednost dp[6][7] postane 4.
Polnjenje zadnje vrstice
Tako dobimo največjo dolžino skupnega podzaporedja kot 4 .
Sledi tabelarična izvedba za problem LCS.
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) { // Initializing a matrix of size // (m+1)*(n+1) int L[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. Note that // L[i][j] contains length of LCS of // X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) if (i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains length of LCS // for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n]; } // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; }>Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int L[][] = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up // fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS // of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X.charAt(i - 1) == Y.charAt(j - 1)) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } return L[m][n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Niz S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Niz S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.length(); int n = S2.length(); System.out.println('Dolžina LCS je' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // To kodo je prispeval Saket Kumar>C## Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): # Declaring the array for storing the dp values L = [[None]*(n+1) for i in range(m+1)] # Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion # Note: L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] # and Y[0..j-1] for i in range(m+1): for j in range(n+1): if i == 0 or j == 0: L[i][j] = 0 elif X[i-1] == Y[j-1]: L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1]+1 else: L[i][j] = max(L[i-1][j], L[i][j-1]) # L[m][n] contains the length of LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n] # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(S1) n = len(S2) print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, m, n)) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)>Javascript// Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int[, ] L = new int[m + 1, n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. // Note that L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i, j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i, j] = L[i - 1, j - 1] + 1; else L[i, j] = max(L[i - 1, j], L[i, j - 1]); } return L[m, n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Koda gonilnika public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Niz S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Dolžina; int n = S2.Dolžina; Console.Write('Dolžina LCS je' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // To kodo je prispeval Sam007>PHP// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem // Utility function to get max of 2 integers function max(a, b) { if (a>b) vrni a; sicer vrni b; } // Vrne dolžino LCS za X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] function lcs(X, Y, m, n) { var L = new Array(m + 1); for(var i = 0; i< L.length; i++) { L[i] = new Array(n + 1); } var i, j; /* Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] */ for(i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for(j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } /* L[m][n] contains length of LCS for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] */ return L[m][n]; } // Driver code var S1 = 'AGGTAB'; var S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; var m = S1.length; var n = S2.length; console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>// Dynamic Programming C# // implementation of LCS problem function lcs($X , $Y, $m, $n) { // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion . // Note: L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for ($i = 0; $i <= $m; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j <= $n; $j++) if ($i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains the length of // LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return $L[$m][$n]; } // Driver Code $S1 = 'AGGTAB'; $S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; $m = strlen($S1); $n = strlen($S2) ; echo 'Length of LCS is '; echo lcs($S1, $S2, $m, $n); // This code is contributed // by Shivi_Aggarwal ?>>
IzhodLength of LCS is 4>Časovna zapletenost: O(m * n), kar je veliko boljše od najslabše možne časovne zapletenosti naivne rekurzivne izvedbe.
Pomožni prostor: O(m * n), ker algoritem uporablja matriko velikosti (m+1)*(n+1) za shranjevanje dolžine skupnih podnizov.Najdaljše skupno podzaporedje (LCS) z uporabo Bottom-Up (Space-Optimization):
- V zgornjem tabelarnem pristopu uporabljamo L[i-1][j] in L[i][j] itd., tukaj se L[i-1] nanaša na prejšnjo vrstico matrike L, L[i] pa na trenutna vrstica.
- Optimizacijo prostora lahko naredimo z uporabo dveh vektorjev, eden je prejšnji in drugi trenutni.
- Ko se notranja zanka for izstopi, inicializiramo prejšnji enak trenutnemu.
Spodaj je izvedba:
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; int longestCommonSubsequence(string& text1, string& text2) { int n = text1.size(); int m = text2.size(); // initializing 2 vectors of size m vectorprev(m + 1, 0), cur(m + 1, 0); za (int idx2 = 0; idx2< m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2); return 0; }> Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.Arrays; public class GFG { public static int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int n = text1.length(); int m = text2.length(); // Initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If matching if (text1.charAt(idx1 - 1) == text2.charAt(idx2 - 1)) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // Not matching else cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = Arrays.copyOf(cur, m + 1); } return cur[m]; } public static void main(String[] args) { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; String S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>C#def longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2): n = len(text1) m = len(text2) # Initializing two lists of size m prev = [0] * (m + 1) cur = [0] * (m + 1) for idx1 in range(1, n + 1): for idx2 in range(1, m + 1): # If characters are matching if text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]: cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1] else: # If characters are not matching cur[idx2] = max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]) prev = cur.copy() return cur[m] if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' # Function call print('Length of LCS is', longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)) # This code is contributed by Rishabh Mathur>Javascriptusing System; class Program { static int LongestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int n = text1.Length; int m = text2.Length; // initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + Math.Max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } static void Main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call Console.WriteLine('Length of LCS is ' + LongestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>function longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2) { const n = text1.length; const m = text2.length; // Initializing two arrays of size m let prev = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); let cur = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); for (let idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { cur[idx2] = 0; } for (let idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (let idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If characters match if (text1[idx1 - 1] === text2[idx2 - 1]) { cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; } // If characters don't match else { cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } } // Update the 'prev' array prev = [...cur]; } return cur[m]; } // Main function function main() { const S1 = 'AGGTAB'; const S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call console.log('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } // Call the main function main();>
IzhodLength of LCS is 4>Časovna zapletenost: O(m * n), ki ostane enak.
Pomožni prostor: O(m), ker algoritem uporablja dve matriki velikosti m.







