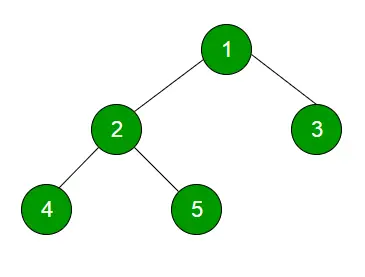
Level Order Traversal Tehnika je definirana kot metoda za prečkanje drevesa, tako da so vsa vozlišča, prisotna na isti ravni, v celoti prečkana pred prečkanjem naslednje ravni.
primer:
Priporočena praksa Prehod vrstnega reda ravni Poskusite!Vnos:
Izhod:
1
23
Štiri
Kako deluje Level Order Traversal?
Glavna ideja prečkanja vrstnega reda ravni je prečkanje vseh vozlišč nižje ravni, preden se premaknete na katero koli od vozlišč višje ravni. To lahko storite na enega od naslednjih načinov:
- naivna (iskanje višine drevesa in prečkanje vsake ravni ter tiskanje vozlišč te ravni)
- učinkovito uporabo čakalne vrste.
Prehod ravni vrstnega reda (naivni pristop):
Najti višina drevesa. Nato za vsako raven zaženite rekurzivno funkcijo z ohranjanjem trenutne višine. Kadarkoli se raven vozlišča ujema, natisnite to vozlišče.
Spodaj je izvedba zgornjega pristopa:
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->podatke<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Izračunajte 'višino' drevesa -- število // vozlišč vzdolž najdaljše poti od korenskega vozlišča // navzdol do najbolj oddaljenega listnega vozlišča. int višina(vozlišče* vozlišče) { if (vozlišče == NULL) vrne 0; else { // Izračunaj višino vsakega poddrevesa int lheight = height(node->left); int desna = višina (vozlišče->desno); // Uporabi večje if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (desno + 1); } } } // Pomožna funkcija, ki dodeli // novo vozlišče z danimi podatki in // NULL levim in desnim kazalcem. vozlišče* novovozlišče(int podatkov) { vozlišče* vozlišče = novo vozlišče(); Vozlišče->podatki = podatki; Vozlišče->levo = NULL; Vozlišče->desno = NULL; vrnitev (vozlišče); } // Koda gonilnika int main() { node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); koren->levo->desno = novoVozlišče(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->podatki); else if (raven> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root->right, level - 1); } } // Izračunajte 'višino' drevesa -- število // vozlišč vzdolž najdaljše poti od korenskega vozlišča // navzdol do najbolj oddaljenega listnega vozlišča int height(struct node* node) { if (vozlišče == NULL) vrni 0; else { // Izračunaj višino vsakega poddrevesa int lheight = height(node->left); int desna = višina (vozlišče->desno); // Uporabi večjega if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); sicer vrni (desno + 1); } } // Pomožna funkcija, ki dodeli novo vozlišče z // danimi podatki in NULL levim in desnim kazalcem. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); vozlišče->podatki = podatki; vozlišče->levo = NULL; vozlišče->desno = NULL; vrnitev (vozlišče); } // Program gonilnika za testiranje zgornjih funkcij int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); koren->levo->desno = novoVozlišče(5); printf('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni binarnega drevesa je
'); printLevelOrder(root); vrni 0; }> Java // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>desna) vrnitev (lvišina + 1); sicer vrni (desno + 1); } } // Natisni vozlišča na trenutni ravni void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) return; if (raven == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (raven> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Program gonilnika za testiranje zgornjih funkcij public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = novo vozlišče (1); tree.root.left = novo vozlišče (2); tree.root.right = novo vozlišče(3); tree.root.left.left = novo vozlišče (4); tree.root.left.right = novo vozlišče(5); System.out.println('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni' + 'binarno drevo je '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # Izračunaj višino drevesa--število vozlišč # vzdolž najdaljše poti od korenskega vozlišča navzdol do # najbolj oddaljenega lista vozlišče def višina(vozlišče): če je vozlišče None: vrni 0 else: # Izračunaj višino vsakega poddrevesa lheight = height(node.left) rheight = height(node.right) # Uporabi večjega, če je lheight> rheight: return lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Program gonilnika za preizkus zgornje funkcije if __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root. left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) print('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni binarnega drevesa je -') printLevelOrder(root) # To kodo je prispeval Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>desna) { return (lvišina + 1); } else { return (desno + 1); } } } // Natisni vozlišča na trenutni ravni public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; } if (nivo == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (raven> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Koda gonilnika public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = novo vozlišče (1); tree.root.left = novo vozlišče (2); tree.root.right = novo vozlišče(3); tree.root.left.left = novo vozlišče (4); tree.root.left.right = novo vozlišče(5); Console.WriteLine('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni ' + 'binarnega drevesa je '); tree.printLevelOrder(); } } // To kodo je prispeval Shrikant13> Javascript // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>desna) vrnitev (lvišina + 1); sicer vrni (desno + 1); } } // Natisni vozlišča na trenutni ravni function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (raven == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (raven> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Program gonilnika za testiranje zgornjih funkcij root = new Node(1); root.left = novo vozlišče (2); root.right = novo vozlišče (3); root.left.left = novo vozlišče (4); root.left.right = novo vozlišče(5); console.log('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni binarnega drevesa je '); printLevelOrder(); // To kodo je prispeval umadevi9616> Izhod
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Časovna zapletenost: O(N), kjer je N število vozlišč v poševnem drevesu.
Pomožni prostor: O(1) Če se upošteva rekurzivni sklad, je uporabljen prostor O(N).
mravlja proti mavenu
Level Order Traversal z uporabo Čakalna vrsta
Obiskati moramo vozlišča na nižji ravni pred katerim koli vozliščem na višji ravni, ta ideja je precej podobna čakalni vrsti. Potisnite vozlišča nižje ravni v čakalni vrsti. Ko je katero koli vozlišče obiskano, izloči to vozlišče iz čakalne vrste in potisni podrejenega vozlišča v čakalno vrsto.
To zagotavlja, da je vozlišče nižje ravni obiskano pred katerim koli vozliščem višje ravni.
Spodaj je izvedba zgornjega pristopa:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Postavi koren v čakalno vrsto in inicializiraj višino q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Natisni začetek čakalne vrste in ga odstrani iz čakalne vrste Node* node = q.front(); cout<< node->podatke<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->levo != NULL) q.push(vozlišče->levo); // V čakalno vrsto postavi desnega podrejenega if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // Pomožna funkcija za ustvarjanje novega vozlišča drevesa Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->podatki = podatki; temp->levo = temp->desno = NULL; povratna temperatura; } // Program gonilnika za testiranje zgornjih funkcij int main() { // Ustvarimo binarno drevo, prikazano v zgornjem diagramu Node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); koren->levo->desno = novoVozlišče(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->podatkov); // Postavi v čakalno vrsto levega podrejenega if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Postavi v čakalno vrsto desni podrejeni if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Odstrani vozlišče iz čakalne vrste in ga naredi za temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Pomožne funkcije struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* rear) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *spredaj = *zadaj = 0; povratna čakalna vrsta; } void enQueue(struct node** queue, int* rear, struct node* new_node) { queue[*rear] = new_node; (*zadaj)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct node** queue, int* front) { (*front)++; povratna čakalna vrsta [*spredaj - 1]; } // Pomožna funkcija, ki dodeli novo vozlišče z // danimi podatki in NULL levim in desnim kazalcem. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); vozlišče->podatki = podatki; vozlišče->levo = NULL; vozlišče->desno = NULL; vrnitev (vozlišče); } // Program gonilnika za testiranje zgornjih funkcij int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); koren->levo->desno = novoVozlišče(5); printf('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni binarnega drevesa je
'); printLevelOrder(root); vrni 0; }> Java // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuečakalna vrsta = nov LinkedList(); queue.add(root); medtem ko (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() odstrani trenutno glavo. Vozlišče tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Postavi v čakalno vrsto levega podrejenega if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // V čakalno vrsto postavi desnega podrejenega if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Ustvarjanje binarnega drevesa in vnos // vozlišč BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = novo vozlišče(1); tree_level.root.left = novo vozlišče(2); tree_level.root.right = novo vozlišče(3); tree_level.root.left.left = novo vozlišče(4); tree_level.root.left.right = novo vozlišče(5); System.out.println('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni binarnega drevesa je - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Natisni začetek čakalne vrste in # ga odstrani iz čakalne vrste print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # V čakalno vrsto postavi levega otroka, če node.left ni None: queue.append(node.left) # V čakalno vrsto vnesite desni podrejeni element, če node.right ni None: queue.append(node.right) # Program gonilnika za preizkus zgornje funkcije, če je __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Vozlišče(2) root.right = Vozlišče(3) root.left.left = Vozlišče(4) root.left.right = Vozlišče(5) print('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni binarnega drevesa je - ') printLevelOrder(root) # To kodo je prispeval Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuečakalna vrsta = nova čakalna vrsta(); queue.Enqueue(root); medtem ko (queue.Count != 0) { Node tempNode = queue.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Postavi v čakalno vrsto levega podrejenega if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // V čakalno vrsto postavi desnega podrejenega if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Koda gonilnika public static void Main() { // Ustvarjanje binarnega drevesa in vnos // vozlišč BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = novo vozlišče(1); tree_level.root.left = novo vozlišče(2); tree_level.root.right = novo vozlišče(3); tree_level.root.left.left = novo vozlišče(4); tree_level.root.left.right = novo vozlišče(5); Console.WriteLine('Prehod vrstnega reda ravni ' + 'binarnega drevesa je - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // To kodo je prispeval PrinciRaj1992> Javascript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> Izhod
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Časovna zapletenost: O(N), kjer je N število vozlišč v binarnem drevesu.
Pomožni prostor: O(N), kjer je N število vozlišč v binarnem drevesu.