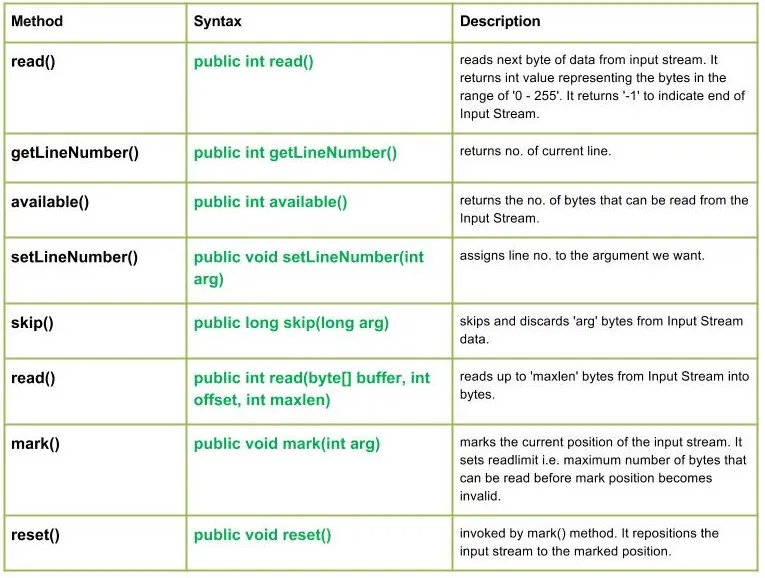
Razred java.io.LineNumberInputStream je preprosto razširitev vhodnega toka, ki zagotavlja dodatno možnost za vodenje evidence trenutne številke vrstice.
Linija je zaporedje bajtov, ki se konča z: 'r', tj. znak za povratni začetek ali znak za novo vrstico: 'n' ali znak za začetek vrstice, ki sledi znaku za povratni začetek.
Izjava:
public class LineNumberInputStream extends Reader
Konstruktorji:
LineNumberInputStream(InputStream in) : Constructs a newline no. stream that reads it's input from the specified Input Stream.
Metode:
Sintaksa:
public int read() Parameters : ------- Return : int value representing the bytes in the range of '0 - 255'. return -1 indicating end of Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Izvedba:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Naslednja koda Java se tukaj ne izvaja, ker ne moremo dostopati do nobene datoteke v spletnem IDE.
Torej kopirajte program v svoj sistem in ga tam zaženite.
The ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v programu, vsebuje:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Izhod:
Hello Geeks. Explaining read() method
Sintaksa:
public int getLineNumber() Parameters : ------- Return : no. of current line
Izvedba:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of getLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try { char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of getLineNumber() : to print line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' At line : ' + a); System.out.print(c); } a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(' at line: ' + a); } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Naslednja koda Java se tukaj ne izvaja, ker ne moremo dostopati do nobene datoteke v spletnem IDE.
Torej kopirajte program v svoj sistem in ga tam zaženite.
The ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v programu, vsebuje:
no. of lines
Izhod:
At line : 0 n At line : 0 o At line : 0 . At line : 0 At line : 0 o At line : 0 f At line : 1 At line : 1 l At line : 1 i At line : 1 n At line : 1 e At line : 1 s at line: 1
Sintaksa:
public int available() Parameters : ------- Return : returns the no. of bytes that can be read from the Input Stream. Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Izvedba:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of available() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of available method : return no. of bytes that can be read a = geekline.available(); System.out.println(c + ' Bytes available : ' + a); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Naslednja koda Java se tukaj ne izvaja, ker ne moremo dostopati do nobene datoteke v spletnem IDE.
Torej kopirajte program v svoj sistem in ga tam zaženite.
The ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v programu, vsebuje:
available
Izhod:
a Bytes available : 4 v Bytes available : 3 a Bytes available : 3 i Bytes available : 2 l Bytes available : 2 a Bytes available : 1 b Bytes available : 1 l Bytes available : 0 e Bytes available : 0
Sintaksa:
public void setLineNumber(int arg) Parameters : arg : line number to assign Return : void Exception: -----
Izvedba:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // Use of setLineNumber() : to set the line no. geekline.setLineNumber(100 + b); // getLineNumber() : returning the current line no. a = geekline.getLineNumber(); System.out.println(c + ' Line No. Set : ' + a); b++; } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Naslednja koda Java se tukaj ne izvaja, ker ne moremo dostopati do nobene datoteke v spletnem IDE.
Torej kopirajte program v svoj sistem in ga tam zaženite.
The ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v programu, vsebuje:
globalna var. v js
LineNumber
Izhod:
L Line No. Set : 100 i Line No. Set : 101 n Line No. Set : 102 e Line No. Set : 103 N Line No. Set : 104 u Line No. Set : 105 m Line No. Set : 106 b Line No. Set : 107 e Line No. Set : 108 r Line No. Set : 109
Sintaksa:
public long skip(long arg) Parameters : arg : no. of bytes of Input Stream data to skip. Return : no. of bytes to be skipped Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Izvedba:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of setLineNumber() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a b = 0; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); while((a = geekline.read()) != -1) { // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; // skip() : to skip and discard 'arg' bytes // Here skip() will skip and discard 3 bytes. geekline.skip(3); System.out.println(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally{ // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Naslednja koda Java se tukaj ne izvaja, ker ne moremo dostopati do nobene datoteke v spletnem IDE.
Torej kopirajte program v svoj sistem in ga tam zaženite.
The ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v programu, vsebuje:
Program Explaining Skip() method
Izhod: '
P r E a n k ) t
Sintaksa:
public int read(byte[] buffer int offset int maxlen) Parameters : buffer : buffer whose data to read offset : starting offset of the data maxlen : max. no. of bytes to read Return : total no. of bytes else return -1 if End of Input Stream is identified Exception: IOException : in case I/O error occurs
Izvedba:
Java// Java program illustrating the working of read() method import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // LineNumberInputStream & FileInputStream initially null LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geekinput = null; try{ char c; int a; // New InputStream : 'ABC' is created geekinput = new FileInputStream('ABC.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geekinput); // read() method returning Bytes of Input Stream as integer // '-1' indicating to read till end Of Input Stream while((a=geekline.read())!=-1) { // Since read() method returns Integer value // So we convert each integer value to char c = (char)a; System.out.print(c); } } catch(Exception e) { // In case of error e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println('ERROR Occurs '); } finally { // Closing the streams Once the End of Input Stream is reached if(geekinput != null) geekinput.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Naslednja koda Java se tukaj ne izvaja, ker ne moremo dostopati do nobene datoteke v spletnem IDE.
Torej kopirajte program v svoj sistem in ga tam zaženite.
The ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v programu, vsebuje:
Read() method
metoda naredi offset = r in maxlen = 5... torej ---tj. 3 odmik, nato 5 bajtov, tj. Branje (nato spet odmik, torej --
Izhod:
The number of char read: 5 ---Read(--
Sintaksa:
public void mark(int arg) Parameters : arg : integer specifying the read limit of the input Stream Return : void
Sintaksa:
public void reset() Parameters : ---- Return : void Exception : -> IOException : If I/O error occurs.
Program Java, ki razlaga metode razreda LineNumberInputStream: reset() in mark()
Java// Java program illustrating the working of LineNumberInputStream method // mark() and reset() import java.io.*; public class NewClass { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { LineNumberInputStream geekline = null; FileInputStream geek = null; try{ geek = new FileInputStream('GEEKS.txt'); geekline = new LineNumberInputStream(geek); // read() method : reading and printing Characters one by one System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); // mark() : read limiting the 'geek' input stream geekline.mark(0); // skip() : it results in reading of 'e' in G'e'eeks geekline.skip(1); System.out.println('skip() method comes to play'); System.out.println('mark() method comes to play'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); boolean check = geekline.markSupported(); if(geekline.markSupported()) { // reset() method : repositioning the stream to marked positions. geekline.reset(); System.out.println('reset() invoked'); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); System.out.println('Char : ' + (char)geekline.read()); } else { System.out.println('reset() method not supported.'); } System.out.println('geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : ' + check); } catch(Exception except) { // in case of I/O error except.printStackTrace(); } finally { // releasing the resources back to the GarbageCollector when closes if(geek != null) geek.close(); if(geekline != null) geekline.close(); } } }
Opomba:
Ta koda se ne bo izvajala v spletnem IDE, ker tukaj ni take datoteke.
To kodo lahko zaženete v svojem sistemu, da preverite delovanje.
ABC.txt datoteka, uporabljena v kodi, ima
HelloGeeks
Izhod:
Char : H Char : e Char : l skip() method comes to play mark() method comes to play Char : o Char : G Char : e reset() method not supported. geekline.markSupported() supported reset() : false