notri Java, dolžina matrike je število elementov, ki jih lahko vsebuje matrika. Ni vnaprej določene metode za pridobitev dolžina niza . Lahko najdemo dolžina polja v Javi z uporabo atributa array dolžina . Ta atribut uporabljamo z imenom polja. V tem razdelku se bomo naučili kako najti dolžino ali velikost polje v Javi .
Atribut dolžine niza
Java zagotavlja atribut dolžina ki določa dolžina niza . Vsak niz ima vgrajeno dolžina lastnost, katere vrednost je velikost matrike. Velikost pomeni skupno število elementov, ki jih lahko vsebuje matrika. Lastnost dolžine lahko prikličete z uporabo operator pika (.). ki mu sledi ime matrike. Najdemo lahko dolžino int[], double[], String[] itd. Na primer:
int[] arr=new int[5]; int arrayLength=arr.length
V zgornjem delčku kode prir je polje tipa int, ki lahko vsebuje 5 elementov. The arrayLength je spremenljivka, ki shrani dolžino matrike. Za iskanje dolžine matrike smo uporabili ime matrike (arr), ki mu je sledil operator pike oziroma atribut dolžine. Določa velikost niza.
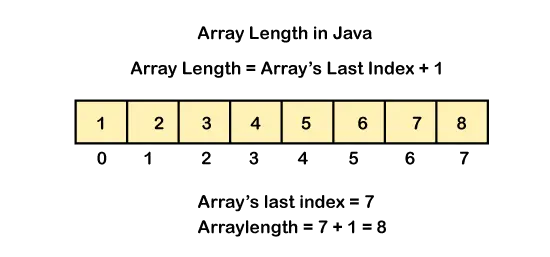
Upoštevajte, da dolžina določa največje število elementov, ki jih lahko vsebuje matrika, ali zmogljivost matrike. Ne šteje elementov, ki so vstavljeni v matriko. To pomeni, da length vrne skupno velikost matrike. Pri nizih, katerih elementi so inicializirani v času ustvarjanja, sta dolžina in velikost enaki.
Če govorimo o logični velikosti, indeksu matrike, potem preprosto int arrayLength=arr.length-1 , ker se matrični indeks začne pri 0. Torej bo logični ali matrični indeks vedno manjši od dejanske velikosti za 1.

Poiščimo dolžino niza s primerom.
ArrayLengthExample1.java
public class ArrayLengthExample1 { public static void main(String[] args) { //defining an array of type int named num //the square bracket contain the length of an array int[] num = new int[10]; //length is an Array attribute that determines the array length int arrayLength=num.length; //prints array length System.out.println('The length of the array is: '+ arrayLength); } } Izhod:
The length of the array is: 10
ArrayLengthExample2.java
public class ArrayLengthExample2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //initializing an array of type String named country String[] country = { 'India', 'Australia', 'Japan', 'USA', 'UAE', 'Canada', 'Brazil'}; //length is an Array attribute that determines the array length int arrayLength=country.length; //prints array length System.out.println('The size of the array is: ' + arrayLength); } } Izhod:
The size of the array is: 7
ArrayLengthExample3.java
public class ArrayLengthExample3 { private static void LengthOfArray(String[] array) { //checks array is empty or not if (array == null) { //if the array is empty prints the following statement System.out.println('The array is empty, can't be determined length.'); } else { //length attribute of the Array class determines the length of an array int arrayLength = array.length; //prints the array length System.out.println('The length of the array is: '+arrayLength); } } public static void main(String[] args) { String[] fruits = { 'Guava', 'Banana', 'Apple', 'Papaya', 'Melon', 'Strawberry'}; String[] alphabets = { 'm', 'p', 'k', 'l', 't' }; String[] numbers = { '12', '25', '63', '84', '90', '11', '54'}; //passing null value to the function LengthOfArray(null); //passing fruits array to the function LengthOfArray(fruits); //passing alphabets array to the function LengthOfArray(alphabets); //passing numbers array to the function LengthOfArray(numbers); } } Izhod:
The array is empty, can't be determined length. The length of the array is: 6 The length of the array is: 5 The length of the array is: 7
