Matrika je fiksne velikosti, homogena struktura podatkov . Omejitev nizov je, da imajo fiksno velikost. To pomeni, da moramo pri deklaraciji matrike določiti število elementov. Tu se pojavi vprašanje, kaj če želimo vstaviti element in ni več prostora za nov element? Tukaj je koncept dinamični niz pride v obstoj. Dinamično poveča velikost polja.
V tem razdelku bomo razumeli kaj je dinamično polje, značilnosti dinamičnega polja, kako spremeniti velikost dinamičnega polja, in kako implementirati dinamično polje v Javi .
Kaj je dinamično polje?
Dinamično polje je a spremenljiva velikost strukturo podatkov seznama. Samodejno se poveča, ko poskušamo vstaviti element, če za nov element ni več prostora. Omogoča nam dodajanje in odstranjevanje elementov. Med izvajanjem dodeljuje pomnilnik z uporabo kopice. Med delovanjem lahko spreminja svojo velikost.
notri Java , ArrayList je izvedba spremenljive velikosti. Implementira vmesnik seznama in nudi vse metode, povezane z operacijami seznama. Moč dinamičnega niza je:
- Hitro iskanje
- Spremenljiva velikost
- Prijazno do predpomnilnika
Delovanje dinamičnega polja
V dinamični matriki so elementi shranjeni neprekinjeno od začetka matrike, preostali prostor pa ostane neuporabljen. Elemente lahko dodajamo, dokler rezervirani razmik ni popolnoma porabljen. Ko je rezerviran prostor porabljen in je treba dodati nekaj elementov. V takem primeru je treba matriko s fiksno velikostjo povečati. Upoštevajte, da preden dodamo element, dodelimo večjo matriko, kopiramo elemente iz matrike in vrnemo novo ustvarjeno matriko.
Drug način za dodajanje elementa je, da najprej ustvarite funkcijo, ki ustvari novo matriko dvojne velikosti, kopira vse elemente iz stare matrike in vrne novo matriko. Podobno lahko zmanjšamo tudi velikost dinamičnega polja.
Velikost v primerjavi z zmogljivostjo
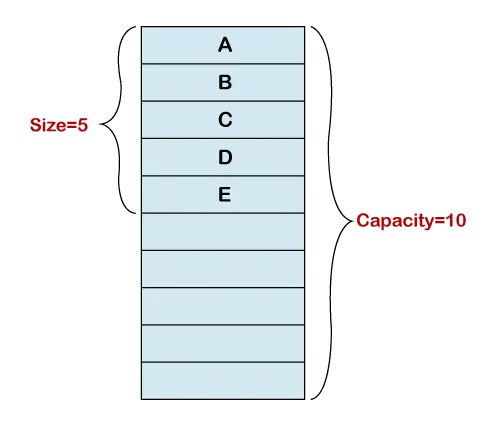
Inicializacija dinamične matrike ustvari matriko fiksne velikosti. Na naslednji sliki ima implementacija matrike 10 indeksov. Matriki smo dodali pet elementov. Zdaj je osnovni niz dolg pet. Zato je dolžina velikosti dinamičnega polja 5, njegova zmogljivost pa 10. Dinamično polje sledi končni točki.
Značilnosti Dynamic Array
V Javi ima dinamično polje tri ključne lastnosti: Dodajte element, izbrišite element in spremenite velikost matrike.
Dodajte element v dinamični niz
V dinamični matriki lahko ustvarimo matriko fiksne velikosti, če želimo v matriko dodati še nekaj elementov. Običajno ustvari novo polje dvojne velikosti. Po tem kopira vse elemente v novo ustvarjeno matriko. Uporabljamo naslednji pristop:

Izbrišite element iz dinamične matrike
Če želimo odstraniti element iz matrike pri podanem indeksu, uporabimo odstraniNa(i) metoda. Metoda razčleni indeksno številko elementa, ki ga želimo izbrisati. Po brisanju elementa premakne preostale elemente (elemente, ki so desno od izbrisanega elementa) v levo od navedene številke indeksa. Uporabljamo tudi metodo remove(), ki izbriše element s konca matrike. Po premiku elementov se shrani 0 v palači zadnjega elementa. Razumejmo to s primerom, kot je prikazano na naslednji sliki.

Spreminjanje velikosti dinamične matrike v Javi
Velikost matrike moramo spremeniti v dveh scenarijih, če:
- Matrika uporablja dodaten pomnilnik, kot je zahtevan.
- Niz zasede ves pomnilnik in dodajati moramo elemente.
V prvem primeru uporabimo srinkSize() način za spreminjanje velikosti niz . Zmanjša velikost niza. Sprosti dodaten ali neuporabljen pomnilnik. V drugem primeru uporabimo growSize() način za spreminjanje velikosti matrike. Poveča velikost niza.
To je draga operacija, ker zahteva večjo matriko in kopira vse elemente iz prejšnje matrike, potem pa vrne novo matriko.

Recimo, da je v zgornji matriki potrebno dodati še šest elementov in v matriki ni več pomnilnika za shranjevanje elementov. V takih primerih povečamo matriko z uporabo growSize() metoda.

Inicializirajte dinamično polje
Inicializacija dinamičnega polja je enaka kot statičnega polja. Razmislite o naslednjem programu Java, ki inicializira dinamično polje.
InitializeDynamicArray.java
public class InitializeDynamicArray { public static void main(String[] args) { //declaring array int array[]; //initialize an array array= new int[6]; //adding elements to the array array[0] = 34; array[1] = 90; array[2] = 12; array[3] = 22; array[4] = 9; array[5] = 27; System.out.print('Elements of Array are: '); //iteraton over the array for(int i=0; i <array.length ; i++) { system.out.print(array[i] +' '); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Elements of Array are: 34 90 12 22 9 27 </pre> <p>Let's implement the operations in a Java program that we have discussed above.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample1.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + ' '); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println('
elements after adding 5:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println('elements of array:'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] ' '); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println('size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println('no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print('
elements element: system.out.print('no. da.count+'
'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;></pre></array.length> Implementirajmo operacije v programu Java, o katerih smo razpravljali zgoraj.
DynamicArrayExample1.java
public class DynamicArrayExample1 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample1() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; creating a function that deletes an element at specified index public void addelementat(int index, int a) compare size with number if not equal grows (count="=" sizeofarray) invoking growsize() method growsize(); for (int i="count" - 1;>= index; i--) { //shifting all the elements to the left from the specified index array[i + 1] = array[i]; } //inserts an element at the specified index array[index] = a; count++; } public static void main(String[] args) { DynamicArrayExample1 da = new DynamicArrayExample1(); //adding elements to the array da.addElement(12); da.addElement(22); da.addElement(35); da.addElement(47); da.addElement(85); da.addElement(26); da.addElement(70); da.addElement(81); da.addElement(96); da.addElement(54); System.out.println('Elements of the array:'); //iterate over the array for accessing the elements for (int i = 0; i <da.sizeofarray; 5 99 i++) { system.out.print(da.array[i] + \' \'); } system.out.println(); determines and prints the size number of elements array system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method to add an element at specified index da.addelementat(5, 99); where is be system.out.println(\'
elements after adding 5:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-6.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <p>Let's shrink the array, delete the last element, and a specified element from the array.</p> <p> <strong>DynamicArrayExample2.java</strong> </p> <pre> public class DynamicArrayExample2 { private int array[]; private int count; private int sizeofarray; //creating a constructor of the class that initializes the values public DynamicArrayExample2() { array = new int[1]; count = 0; sizeofarray = 1; } //creating a function that appends an element at the end of the array public void addElement(int a) { //compares if the number of elements is equal to the size of the array or not if (count == sizeofarray) { //invoking the growSize() method that creates an array of double size growSize(); } //appens an element at the end of the array array[count] = a; count++; } //function that creates an array of double size public void growSize() { //declares a temp[] array int temp[] = null; if (count == sizeofarray) { //initialize a double size array of array temp = new int[sizeofarray * 2]; { for (int i = 0; i <sizeofarray; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="sizeofarray" * 2; method removes unused space public void shrinksize() declares a temp[] int if (count> 0) { //creates an array of the size equal to the count i.e. number of elements the array have temp = new int[count]; for (int i = 0; i <count; i++) { copies all the elements of old array temp[i]="array[i];" } sizeofarray="count;" creating a function that removes last for public void removeelement() if (count> 0) { array[count - 1] = 0; count--; } } //creating a function that delets an element from the specified index public void removeElementAt(int index) { if (count > 0) { for (int i = index; i <count 7 - 1; i++) { shifting all the elements to left from specified index array[i]="array[i" + 1]; } array[count 1]="0;" count--; public static void main(string[] args) dynamicarrayexample2 da="new" dynamicarrayexample2(); adding array da.addelement(12); da.addelement(22); da.addelement(35); da.addelement(47); da.addelement(85); da.addelement(26); da.addelement(70); da.addelement(81); da.addelement(96); da.addelement(54); system.out.println(\'elements of array:\'); iterate over for accessing (int i="0;" < da.sizeofarray; system.out.print(da.array[i] \' \'); system.out.println(); determines and prints size number system.out.println(\'size array: da.sizeofarray); system.out.println(\'no. in da.count); invoking method delete last element da.removeelement(); after deleting system.out.print(\'
elements element: system.out.print(\'no. da.count+\'
\'); that deletes an da.removeelementat(7); at 7: pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/java-tutorial/02/dynamic-array-java-7.webp" alt="Dynamic Array in Java"> <hr></count></count;></sizeofarray;></pre></da.sizeofarray;></sizeofarray;>