V C++ je dedovanje proces, v katerem en objekt samodejno pridobi vse lastnosti in obnašanja svojega nadrejenega objekta. Na ta način lahko znova uporabite, razširite ali spremenite atribute in vedenja, ki so definirana v drugem razredu.
V C++ se razred, ki podeduje člane drugega razreda, imenuje izpeljani razred, razred, katerega člani so podedovani, pa osnovni razred. Izpeljani razred je specializiran razred za osnovni razred.
Prednost dedovanja C++
Ponovna uporabnost kode: Zdaj lahko znova uporabite člane svojega nadrejenega razreda. Člana torej ni treba ponovno definirati. Zato je v razredu potrebno manj kode.
odpreti datoteko z javo
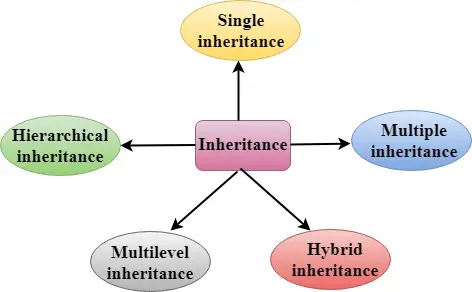
Vrste dedovanja
C++ podpira pet vrst dedovanja:
- Enkratno dedovanje
- Večkratno dedovanje
- Hierarhično dedovanje
- Večnivojsko dedovanje
- Hibridno dedovanje
Izpeljani razredi
Izpeljani razred je definiran kot razred, izpeljan iz osnovnega razreda.
kako pretvoriti int v niz java
Sintaksa izpeljanega razreda:
|_+_|V zgornjem primeru funkcija izpeljanega razreda preglasi metodo osnovnega razreda. Zato bo klic funkcije display() preprosto poklical funkcijo, definirano v izpeljanem razredu. Če želimo priklicati funkcijo osnovnega razreda, lahko uporabimo operator razrešitve razreda.
int main() { B b; b.display(); // Calling the display() function of B class. b.B :: display(); // Calling the display() function defined in B class. } Hibridno dedovanje C++
Hibridno dedovanje je kombinacija več kot ene vrste dedovanja.

Poglejmo preprost primer:
#include using namespace std; class A { protected: int a; public: void get_a() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'a' : ' <>a; } }; class B : public A { protected: int b; public: void get_b() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of 'b' : ' <>b; } }; class C { protected: int c; public: void get_c() { std::cout << 'Enter the value of c is : ' <>c; } }; class D : public B, public C { protected: int d; public: void mul() { get_a(); get_b(); get_c(); std::cout << 'Multiplication of a,b,c is : ' < <a*b*c<< std::endl; } }; int main() { d d; d.mul(); return 0; < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the value of 'a' : 10 Enter the value of 'b' : 20 Enter the value of c is : 30 Multiplication of a,b,c is : 6000 </pre> <h2>C++ Hierarchical Inheritance</h2> <p>Hierarchical inheritance is defined as the process of deriving more than one class from a base class.</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/62/c-inheritance-7.webp" alt="C++ Inheritance"> <p> <strong>Syntax of Hierarchical inheritance:</strong> </p> <pre> class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } </pre> <p>Let's see a simple example:</p> <pre> #include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<></pre></a*b*c<<> Hierarhično dedovanje C++
Hierarhično dedovanje je definirano kot postopek izpeljave več kot enega razreda iz osnovnega razreda.

Sintaksa hierarhičnega dedovanja:
class A { // body of the class A. } class B : public A { // body of class B. } class C : public A { // body of class C. } class D : public A { // body of class D. } Poglejmo preprost primer:
sort arraylist v Javi
#include using namespace std; class Shape // Declaration of base class. { public: int a; int b; void get_data(int n,int m) { a= n; b = m; } }; class Rectangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int rect_area() { int result = a*b; return result; } }; class Triangle : public Shape // inheriting Shape class { public: int triangle_area() { float result = 0.5*a*b; return result; } }; int main() { Rectangle r; Triangle t; int length,breadth,base,height; std::cout << 'Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: ' <>length>>breadth; r.get_data(length,breadth); int m = r.rect_area(); std::cout << 'Area of the rectangle is : ' <<m<< std::endl; std::cout << \\'enter the base and height of triangle: \\' <>base>>height; t.get_data(base,height); float n = t.triangle_area(); std::cout <<\\'area of the triangle is : \\' << n<<std::endl; return 0; } < pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Enter the length and breadth of a rectangle: 23 20 Area of the rectangle is : 460 Enter the base and height of the triangle: 2 5 Area of the triangle is : 5 </pre></\\'area></m<<>