Ta vadnica se bo naučila, kako lahko uporabimo algoritem binarnega iskanja z uporabo Pythona, da poiščemo položaj indeksa elementa na danem seznamu.
Uvod
Binarno iskanje je algoritem za iskanje določenega elementa na seznamu. Recimo, da imamo seznam tisoč elementov in moramo dobiti položaj indeksa določenega elementa. Z algoritmom binarnega iskanja lahko zelo hitro najdemo položaj indeksa elementa.
če drugače v javi
Obstaja veliko iskalnih algoritmov, vendar je binarno iskanje najbolj priljubljeno med njimi.
Elemente na seznamu je treba razvrstiti, da se uporabi algoritem binarnega iskanja. Če elementi niso razvrščeni, jih najprej razvrstite.
Razumejmo koncept binarnega iskanja.
Koncept binarnega iskanja
V binarnem iskalnem algoritmu lahko najdemo položaj elementa z naslednjimi metodami.
- Rekurzivna metoda
- Iterativna metoda
Tehniki pristopa deli in vladaj sledi rekurzivna metoda. Pri tej metodi se funkcija znova in znova kliče sama, dokler ne najde elementa na seznamu.
Niz stavkov se večkrat ponovi, da se najde položaj indeksa elementa v iterativni metodi. The medtem za izpolnitev te naloge.
Binarno iskanje je učinkovitejše od linearnega iskanja, ker nam ni treba iskati po indeksu vsakega seznama. Seznam mora biti razvrščen, da se doseže binarni iskalni algoritem.
Oglejmo si korak za korakom implementacijo binarnega iskanja.
Imamo razvrščen seznam elementov in iščemo položaj indeksa 45.
[12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54]
Torej, na naš seznam postavljamo dva kazalca. En kazalec se uporablja za označevanje klicane manjše vrednosti nizka in drugi kazalec se uporablja za označevanje najvišje klicane vrednosti visoka .
Nato izračunamo vrednost sredina element v matriki.
mid = (low+high)/2 Here, the low is 0 and the high is 7. mid = (0+7)/2 mid = 3 (Integer)
Zdaj bomo iskani element primerjali s srednjo vrednostjo indeksa. V tem primeru, 32 ni enako Štiri. Zato moramo opraviti nadaljnjo primerjavo, da najdemo element.
Če je številka, ki jo iščemo, enaka sredini. Potem se vrni sredina sicer preidite na nadaljnjo primerjavo.
Število za iskanje je večje od sredina število, primerjamo n s srednjim elementom elementov na desni strani sredina in nastavite nizko na nizka = srednja + 1.
V nasprotnem primeru primerjajte n z srednji element elementov na levi strani sredina in nastavite visoka do visoko = srednje - 1.
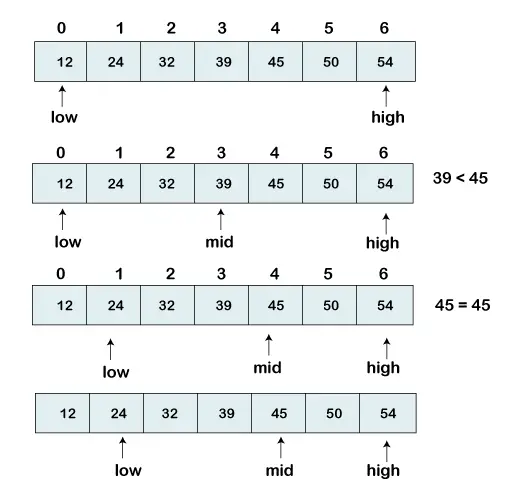
Ponavljajte, dokler ne najdete številke, ki jo iščemo.
Izvedite binarno iskanje v Pythonu
Najprej implementiramo binarno iskanje z iterativno metodo. Ponovili bomo niz stavkov in ponovili vsako postavko seznama. Srednjo vrednost bomo našli, dokler iskanje ni končano.
Razumejmo naslednji program iterativne metode.
Implementacija Python
# Iterative Binary Search Function method Python Implementation # It returns index of n in given list1 if present, # else returns -1 def binary_search(list1, n): low = 0 high = len(list1) - 1 mid = 0 while low <= 1 2 high: # for get integer result mid="(high" + low) check if n is present at list1[mid] n: high="mid" - smaller, compared to the left of else: return element was not in list, -1 initial list1 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] function call n) !="-1:" print('element index', str(result)) list1') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 4 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>In the above program -</p> <ul> <li>We have created a function called <strong>binary_search()</strong> function which takes two arguments - a list to sorted and a number to be searched.</li> <li>We have declared two variables to store the lowest and highest values in the list. The low is assigned initial value to 0, <strong>high</strong> to <strong>len(list1)</strong> - 1 and mid as 0.</li> <li>Next, we have declared the <strong>while</strong> loop with the condition that the <strong>lowest</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>highest</strong> The while loop will iterate if the number has not been found yet.</li> <li>In the while loop, we find the mid value and compare the index value to the number we are searching for.</li> <li>If the value of the mid-index is smaller than <strong>n</strong> , we increase the mid value by 1 and assign it to The search moves to the left side.</li> <li>Otherwise, decrease the mid value and assign it to the <strong>high</strong> . The search moves to the right side.</li> <li>If the n is equal to the mid value then return <strong>mid</strong> .</li> <li>This will happen until the <strong>low</strong> is equal and smaller than the <strong>high</strong> .</li> <li>If we reach at the end of the function, then the element is not present in the list. We return -1 to the calling function.</li> </ul> <p>Let's understand the recursive method of binary search.</p> <h2>Recursive Binary Search</h2> <p>The recursion method can be used in the binary search. In this, we will define a recursive function that keeps calling itself until it meets the condition.</p> <p>Let's understand the above program using the recursive function.</p> <h3>Python Program</h3> <pre> # Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Element is present at index 2 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation</strong> </p> <p>The above program is similar to the previous program. We declared a recursive function and its base condition. The condition is the lowest value is smaller or equal to the highest value.</p> <ul> <li>We calculate the middle number as in the last program.</li> <li>We have used the <strong>if</strong> statement to proceed with the binary search.</li> <li>If the middle value equal to the number that we are looking for, the middle value is returned.</li> <li>If the middle value is less than the value, we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and increase the mid value by one and assign to low.</li> <li>If the middle value is greater than the value we are looking then our recursive function <strong>binary_search()</strong> again and decrease the mid value by one and assign it to low.</li> </ul> <p>In the last part, we have written our main program. It is the same as the previous program, but the only difference is that we have passed two parameters in the <strong>binary_search()</strong> function.</p> <p>This is because we can't assign the initial values to the low, high and mid in the recursive function. Every time the recursive is called the value will be reset for those variables. That will give the wrong result.</p> <h2>Complexity</h2> <p>The complexity of the binary search algorithm is <strong>O(1)</strong> for the best case. This happen if the element that element we are looking find in the first comparison. The <strong>O(logn)</strong> is the worst and the average case complexity of the binary search. This depends upon the number of searches are conducted to find the element that we are looking for.</p> <h2>Conclusion</h2> <p>A binary search algorithm is the most efficient and fast way to search an element in the list. It skips the unnecessary comparison. As the name suggests, the search is divided into two parts. It focuses on the side of list, which is close to the number that we are searching.</p> <p>We have discussed both methods to find the index position of the given number.</p> <hr></=> Pojasnilo:
V zgornjem programu -
- Ustvarili smo funkcijo imenovano binarno_iskanje() funkcija, ki sprejme dva argumenta - seznam za razvrščanje in število za iskanje.
- Razglasili smo dve spremenljivki za shranjevanje najnižje in najvišje vrednosti na seznamu. Nizki je dodeljena začetna vrednost 0, visoka do len (seznam1) - 1 in sredina kot 0.
- Nato smo razglasili medtem zanke s pogojem, da je najnižja je enako in manjše od najvišja Zanka while se bo ponovila, če številka še ni bila najdena.
- V zanki while poiščemo srednjo vrednost in primerjamo vrednost indeksa s številom, ki ga iščemo.
- Če je vrednost srednjega indeksa manjša od n , povečamo srednjo vrednost za 1 in jo dodelimo Iskanje se premakne na levo stran.
- V nasprotnem primeru zmanjšajte srednjo vrednost in jo dodelite visoka . Iskanje se premakne na desno stran.
- Če je n enak srednji vrednosti, vrni sredina .
- To se bo dogajalo do nizka je enako in manjše od visoka .
- Če pridemo do konca funkcije, elementa ni na seznamu. Klicni funkciji vrnemo -1.
Razumejmo rekurzivno metodo binarnega iskanja.
Rekurzivno binarno iskanje
Rekurzijsko metodo lahko uporabimo pri binarnem iskanju. V tem bomo definirali rekurzivno funkcijo, ki kliče sama sebe, dokler ne izpolni pogoja.
cpld proti FPGA
Razumejmo zgornji program z uporabo rekurzivne funkcije.
Program Python
# Python program for recursive binary search. # Returns index position of n in list1 if present, otherwise -1 def binary_search(list1, low, high, n): # Check base case for the recursive function if low n: return binary_search(list1, low, mid - 1, n) # Else the search moves to the right sublist1 else: return binary_search(list1, mid + 1, high, n) else: # Element is not available in the list1 return -1 # Test list1ay list1 = [12, 24, 32, 39, 45, 50, 54] n = 32 # Function call res = binary_search(list1, 0, len(list1)-1, n) if res != -1: print('Element is present at index', str(res)) else: print('Element is not present in list1')
Izhod:
Element is present at index 2
Pojasnilo
Zgornji program je podoben prejšnjemu programu. Razglasili smo rekurzivno funkcijo in njen osnovni pogoj. Pogoj je, da je najnižja vrednost manjša ali enaka najvišji vrednosti.
- Srednjo številko izračunamo kot v zadnjem programu.
- Uporabili smo če stavek za nadaljevanje binarnega iskanja.
- Če je srednja vrednost enaka številu, ki ga iščemo, se vrne srednja vrednost.
- Če je srednja vrednost manjša od vrednosti, iščemo našo rekurzivno funkcijo binarno_iskanje() znova in povečajte srednjo vrednost za eno ter dodelite nizki.
- Če je srednja vrednost večja od vrednosti, ki jo iščemo, je naša rekurzivna funkcija binarno_iskanje() znova in znižajte srednjo vrednost za eno ter jo dodelite nizki.
V zadnjem delu smo napisali naš glavni program. Je enak kot prejšnji program, vendar je edina razlika v tem, da smo posredovali dva parametra v binarno_iskanje() funkcijo.
To je zato, ker v rekurzivni funkciji ne moremo dodeliti začetnih vrednosti nizki, visoki in srednji vrednosti. Vsakič, ko se rekurziv pokliče, bo vrednost teh spremenljivk ponastavljena. To bo dalo napačen rezultat.
Kompleksnost
Kompleksnost binarnega iskalnega algoritma je O(1) v najboljšem primeru. To se zgodi, če element, ki ga iščemo, najdemo v prvi primerjavi. The O (prijava) je najslabša in povprečna zapletenost binarnega iskanja. To je odvisno od števila iskanj, izvedenih za iskanje elementa, ki ga iščemo.
Zaključek
Binarni iskalni algoritem je najučinkovitejši in najhitrejši način iskanja elementa na seznamu. Preskoči nepotrebno primerjavo. Kot že ime pove, je iskanje razdeljeno na dva dela. Osredotoči se na stran seznama, ki je blizu številke, ki jo iščemo.
Razpravljali smo o obeh metodah za iskanje položaja indeksa danega števila.
